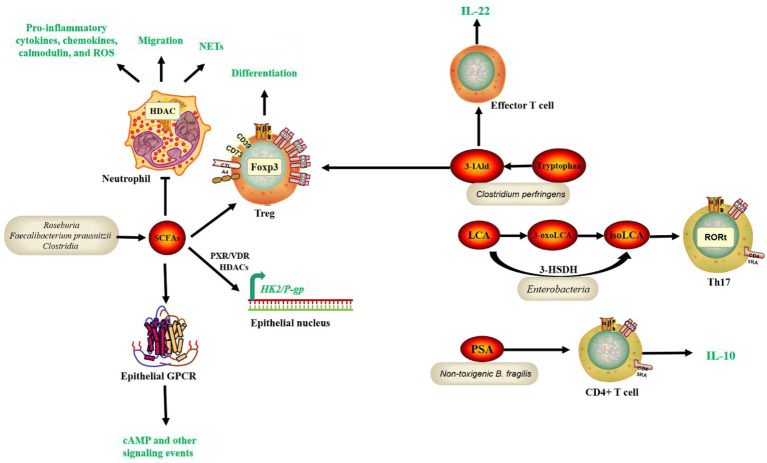
Figure 1.
Common bacteria species and functional pathways involved in the protection of IBD. SCFAs, tryptophan, and bile acid metabolites, and PSA production by gut microbiota interact with receptors on IECs and immune cells, contributing to gene regulation, epithelial function, and homeostasis maintenance and inflammation modulation, thus leading to alleviation of IBD symptoms. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), Polysaccharide A (PSA), Histone deacetylase (HDAC), Foxhead box P3 (Foxp3), Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), Hexokinase 2 (HK2), P-glycoprotein (P-gp), Intestinal epithelial cells (IECs), Pregnane X receptor (PXR), Vitamin D3 receptor (VDR), Helper T-cell 17 (Th17), 3-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3-HSDH), Retinoid-related orphan receptor gamma t (RORt), indole-3-carboxaldehyde (3-IAld), Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (Ahr).