Figure 2. Intracellular actions of metformin.
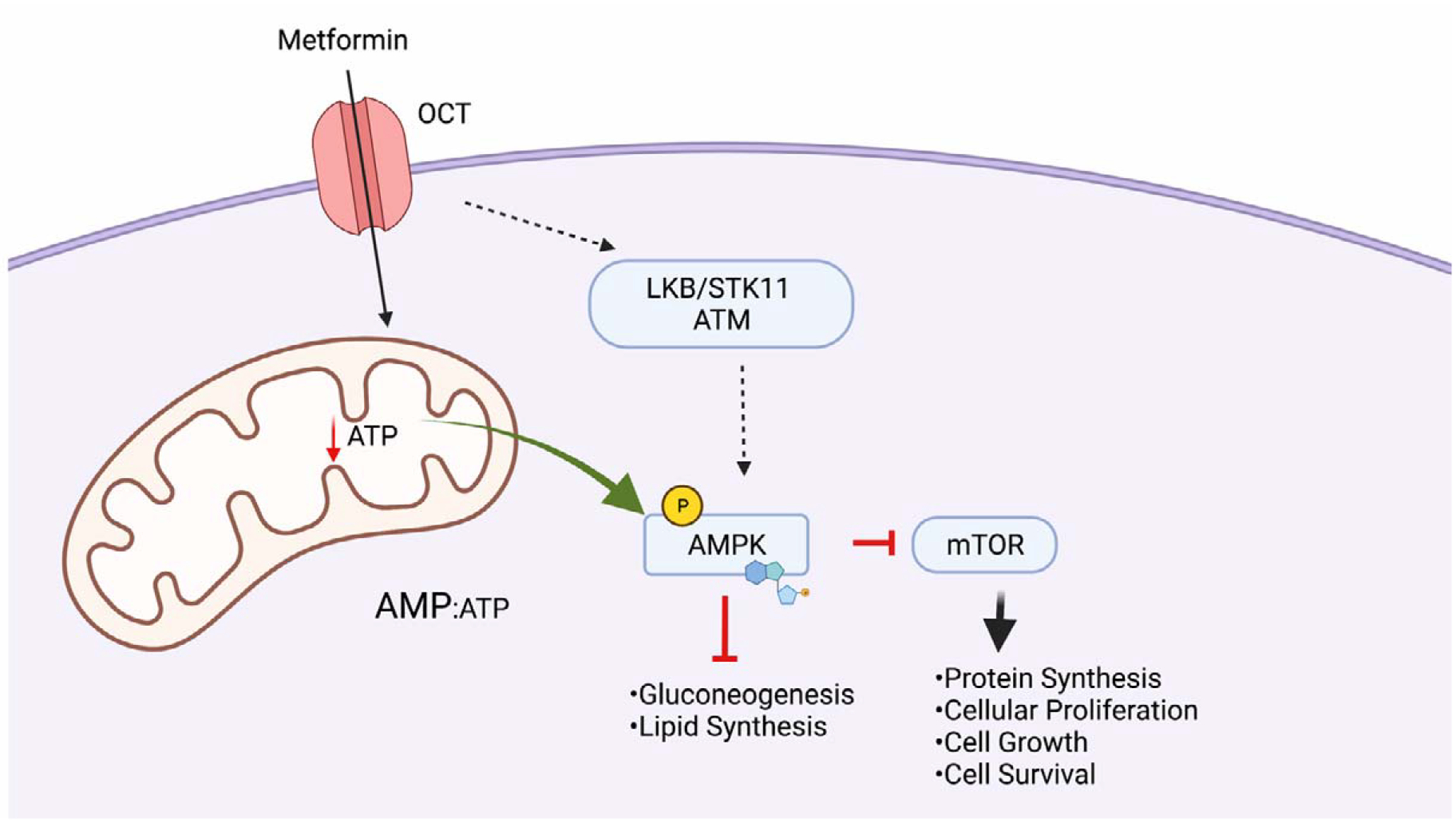
Metformin enters the cell via organic cation transporters (OCT). Following entry, the cellular redox status results in phosphorylation of AMPK by intracellular kinases LKB/ATM/ STK11. Reduced ATP production by metformin-mediated Complex I inhibition in mitochondria also results in activation of AMPK via increased AMP:ATP ration. Activation of AMPK reduces anabolism in cells via downstream targets, ultimately inhibiting cell growth. Created with Biorender.com
