Figure 2:
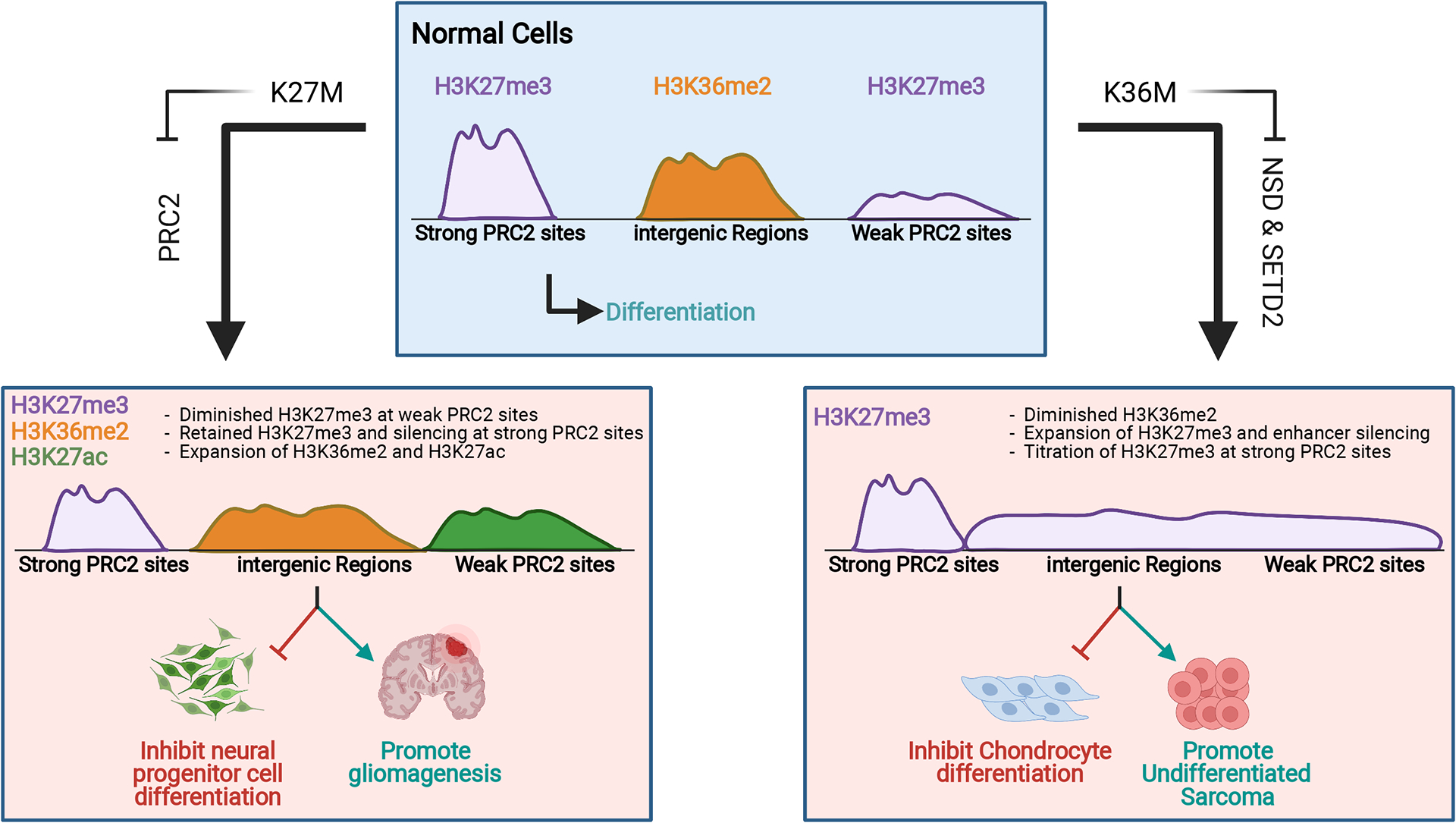
Epigenome reprogramming by “K-to-M” H3 mutations. In H3K27M mutant cells (left), inhibition of PRC2 leads to diminished H3K27me3 and increased expression of weak PRC2 target genes. Strong PRC2 target genes retain H3K27me3 and remain silenced. Loss of global H3K27me3 is also accompanied by expansion of H3K36me2 domains and pervasive increases in H3K27ac. In H3K36M mutant cells (right), inhibition of NSD family enzymes leads to diminished H3K36me2. Spreading of H3K27me3 into H3K36me2 domains results in enhancer silencing. The genome-wide H3K27me3 increase also has a “diluting” effect on strong PRC2 target genes, leading to their de-repression.
