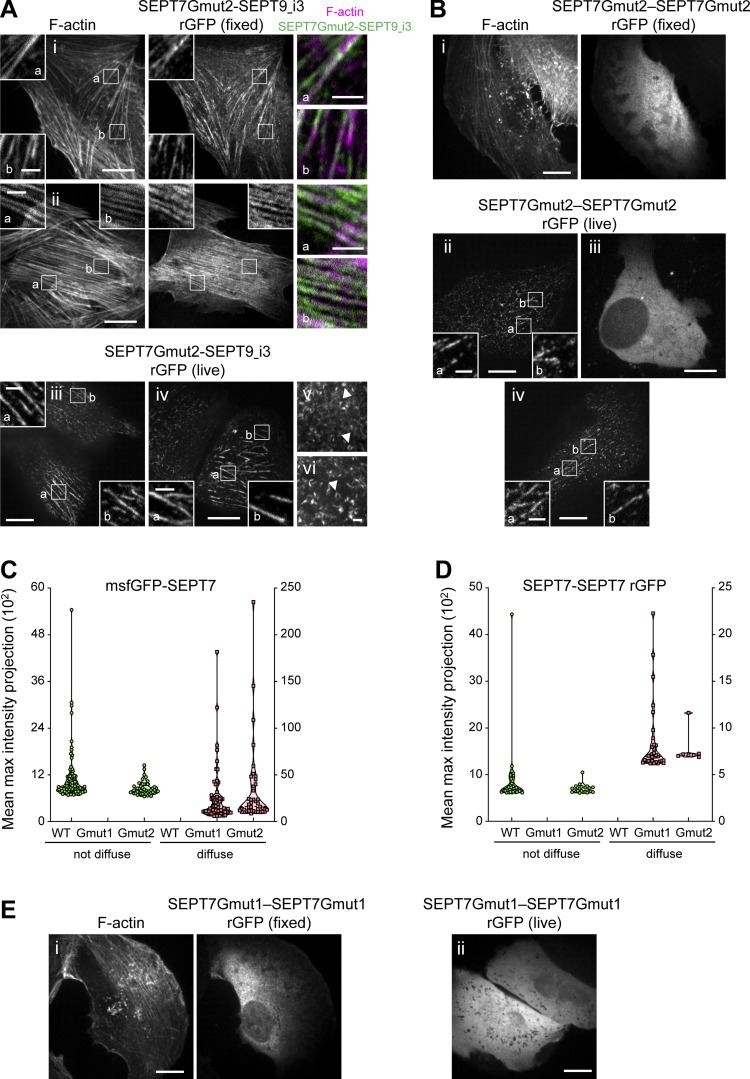
Figure 6.
Intact SEPT7 G interfaces are required for septin localization to SFs. (A) Representative examples of fixed (i and ii) and live (iii–vi) GFP1-9 cells co-expressing β11-SEPT7Gmut2 and SEPT9_i3-β10. Fixed cells are co-stained for F-actin (phalloidin). Examples shows rGFP localizing (i and ii) to ventral SFs (a and b), (iii) to perinuclear actin caps (a and b), (iv) to ventral SFs (a and b), and (v and vi) rings (arrowheads). Scale bars in large fields of views, 10 μm. Scale bars in insets, 2 μm. (B) Representative examples of GFP1-9 cells (i–iv) co-expressing β10- and β11-SEPT7Gmut2. The fixed cell is co-stained for F-actin (phalloidin). Examples show diffuse cytosolic phenotypes (i and iii) of the rGFP and rGFP localizing to SFs (ii and iv). Scale bars in large fields of views, 10 μm. Scale bars in insets, 2 μm. (C) Violin plots depicting the distribution of diffuse cytosolic (red datapoints) vs. non-diffuse (green datapoints) phenotypes as a function of the intensity of the msfGFP signal in cells expressing wild-type msfGFP-SEPT7 or msfGFP-SEPT7NCmut. Data points are from a total of 71 cells for wild-type, 68 cells for SEPT7Gmut1 and 90 cells for SEPT7Gmut2 distributed among the two phenotypes. (D) Violin plots depicting the distribution of diffuse cytosolic (red datapoints) vs. non-diffuse (green datapoints) phenotypes as a function of the intensity of the rGFP signal in GFP1-9 cells co-expressing wild-type β10- and β11-SEPT7, β10- and β11-SEPT7Gmut1, or β10- and β11-SEPT7Gmut2. Data points are from a total of 40 cells for wild-type, 33 cells for β10- and β11-SEPT7Gmut1 and 29 cells for β10- and β11-SEPT7Gmut2 distributed among the two phenotypes. (E) Representative examples of GFP1-9 cells (i and ii) co-expressing β10- and β11-SEPT7Gmut1 showing a diffuse cytosolic phenotype. The fixed cell is co-stained for F-actin (phalloidin). Scale bar, 10 μm.