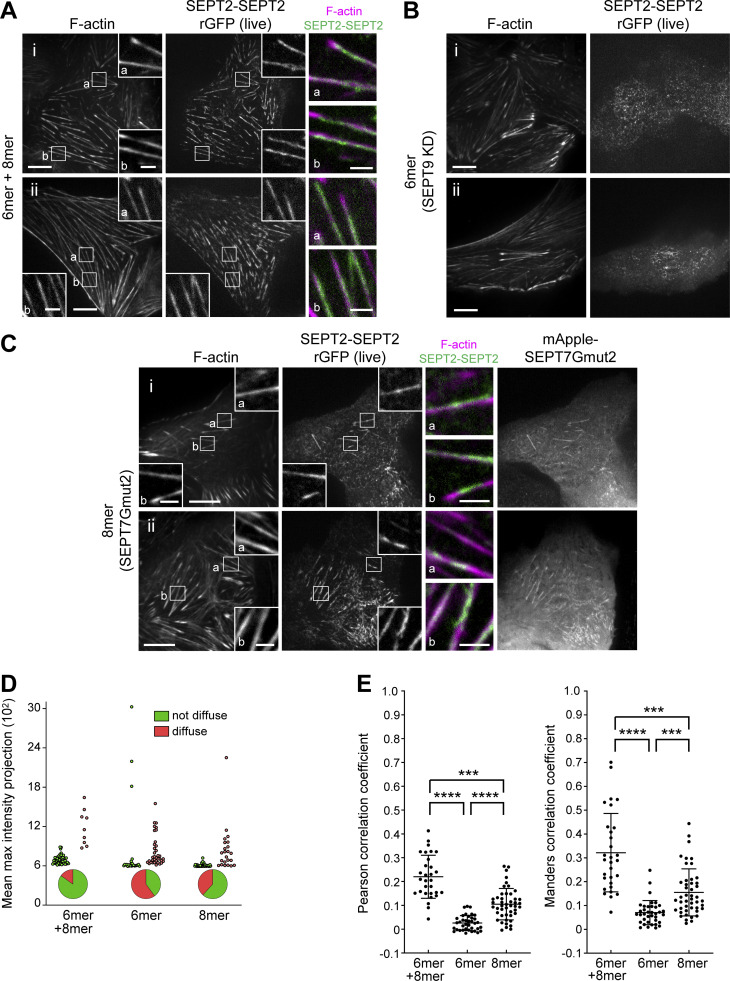
Figure 7.
Septin octamers are essential for the integrity of SF-associated septin filaments. (A–C) Representative confocal micrographs of SEPT2-SEPT2 rGFP distribution in live cells co-labeled for F-actin (SiR-actin). Cells were treated with siRNA targeting SEPT2 (A), with siRNAs targeting both SEPT2 and SEPT9 (B), or with siRNA targeting both SEPT2 and SEPT7 and co-transfected with mApple-SEPT7Gmut2 (C). Examples in A and C show rGFP localizing to ventral SFs (a and b). Scale bars in large fields of views, 10 μm. Scale bars in insets, 2 μm. (D) Scatter dot plots depicting the distribution of diffuse cytosolic (red datapoints) vs. non-diffuse (green datapoints) phenotypes in cells under the same conditions as in A–C, also shown as pie graphs. Data points are from a total of 59 cells for wild-type and 60 cells for each perturbation condition, distributed among the two phenotypes. (E) Scatter dot plots (mean ± SD) depicting the distributions of calculated Pearson (left) and Manders (right) correlation coefficients for actin-septin colocalization in cells under the same conditions as in A–C. Data points for each plot, from left to right, are from a total of 30, 37, and 46 cells, respectively. Kruskal–Wallis test; *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001.