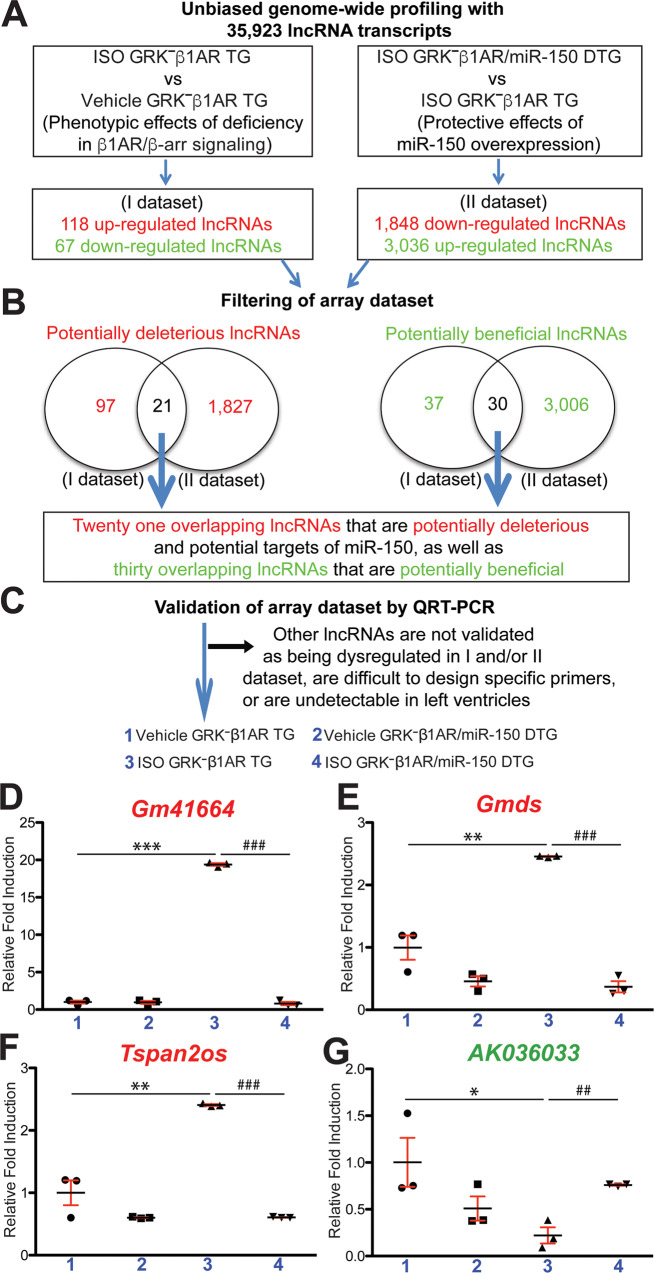
Fig. 4. Genome-wide long noncoding RNA profiling in GRK−β1AR TG and GRK−β1AR;miR-150 DTG mice identifies novel long noncoding RNAs that are controlled by β1AR/β-arrestin-mediated signaling and regulate miR-150.
A, B Genome-wide profiling and filtering strategies of array dataset based on the correlation between transcript signatures and cardiac phenotypes. Twenty-one dysregulated (DE) long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), which are upregulated in the I dataset (ISO GRK−β1AR TG compared to vehicle GRK−β1AR TG controls) but are downregulated in the II dataset (ISO GRK−β1AR;miR-150 DTG compared to ISO GRK−β1AR TG) at 1-week post-treatment, were chosen for further analyses. Thirty other DE lncRNAs, which are downregulated in the I dataset (ISO GRK−β1AR TG compared to vehicle GRK−β1AR TG controls) but are upregulated in the II dataset (ISO GRK−β1AR;miR-150 DTG compared to ISO GRK−β1AR TG) at 1-week post-treatment, were chosen for further analyses. N = 3 per group. C–G Validation strategy of array dataset. Three potentially deleterious DE lncRNAs (Gm41664, Gmds, and Tspan2os) were validated by QRT-PCR analyses in LVs from GRK−β1AR TG and GRK−β1AR;miR-150 DTG mice at 1-week post-treatment (D–F). The other potentially beneficial DE lncRNA (AK036033) was validated by QRT-PCR analyses in LVs from GRK−β1AR TG and GRK−β1AR;miR-150 DTG mice at 1-week post-treatment (G). Of note, other lncRNAs are not validated as being dysregulated as presented in (B), are difficult to design specific primers, or are undetectable in LVs. Data are shown as fold induction of lncRNA expression normalized to Gapdh. N = 3 per group. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparison test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, or ***P < 0.001 vs. vehicle; ##P < 0.01 or ###P < 0.001 vs. ISO GRK−β1AR TG. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.