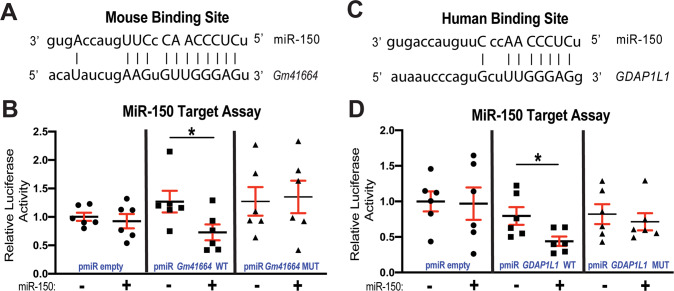
Fig. 6. MiR-150 interacts with Gm41664 and GDAP1L1.
A Mouse Gm41664 has the strongest miR-150 binding site with 12-mer complementary sequences. MiR-150 seed pairing in the target region and complementary sequences outside the seed region are presented as vertical lines. B MiR-150’s capability of directly repressing the activity of luciferase (LUC) reporter constructs that include either wild-type (WT) or mutated (MUT) binding sites for Gm41664. Transfection with or without miR-150 mimic in H9c2 cells is shown as + or −. The LUC activity of Firefly was normalized to the LUC activity of Renilla and compared with empty vector measurements. N = 6. Unpaired two-tailed t-test. C Human GDAP1L1 has a conserved miR-150 binding site in the 3’-untranslated region (3’UTR). MiR-150 seed pairing in the target region and complementary sequences outside the seed region are presented as vertical lines. D The direct ability of miR-150 to inhibit the activity of LUC reporter constructs that include either WT or MUT binding sites for GDAP1L1. Transfection with or without miR-150 mimic in AC16 cells is indicated as + or −. The LUC activity of Firefly was normalized to the LUC activity of Renilla and compared to empty vector measurements. N = 6. Unpaired two-tailed t-test. *P < 0.05 vs. miR mimic control.