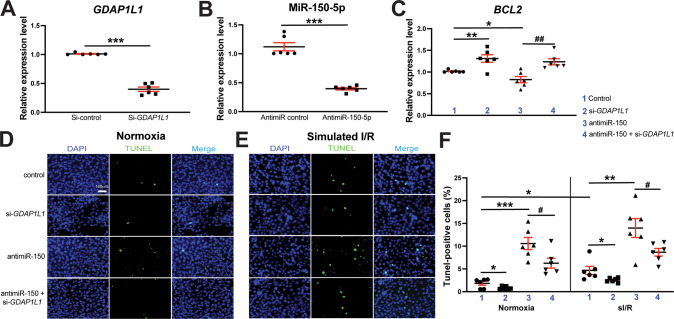
Fig. 8. GDAP1L1 is required for miR-150-dependent inhibition of human cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
A, B AC16 cells were transfected with control scramble siRNA (si-control) or GDAP1L1 siRNA (si-GDAP1L1) (A) and with anti-miR control scramble or anti-miR-150 (B). QRT-PCR for GDAP1L1 (A) or miR-150 (B) was conducted to check the knockdown efficiency. Data were normalized to GAPDH (A) or U6 SNRNA (B) and expressed relative to controls. N = 6 per group. Unpaired two-tailed t-test. ***P < 0.001 vs. si-control or anti-miR control. C QRT-PCR expression analysis of anti-apoptotic BCL2 in human cardiomyocytes (HuCMs) transfected with 4 different groups as indicated. N = 6. BCL2 expression compared to GAPDH was calculated using 2−ΔΔCt, and data are presented as fold induction of BCL2 expression levels normalized to control (si-control or anti-miR control). One-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparison test. *P < 0.05 or **P < 0.01 vs. control. ##P < 0.01 vs. anti-miR-150. D–F RNA interference with GDAP1L1 protects HuCMs from the pro-apoptotic effects mediated by anti-miR-150. HuCMs were transfected as indicated and subjected to in vitro simulation of I/R (hypoxia/reoxygenation) [sI/R (H/R)]. TUNEL assays were then conducted in both normoxic (D, F) and sI/R conditions (E, F). Scale bar = 100 μm. The percentage of apoptotic nuclei (green) was calculated after the normalization of total nuclei (blue). N = 6. One-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparison test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, or ***P < 0.001 vs. control. #P < 0.05 vs. anti-miR-150. All data are shown as mean ± SEM.