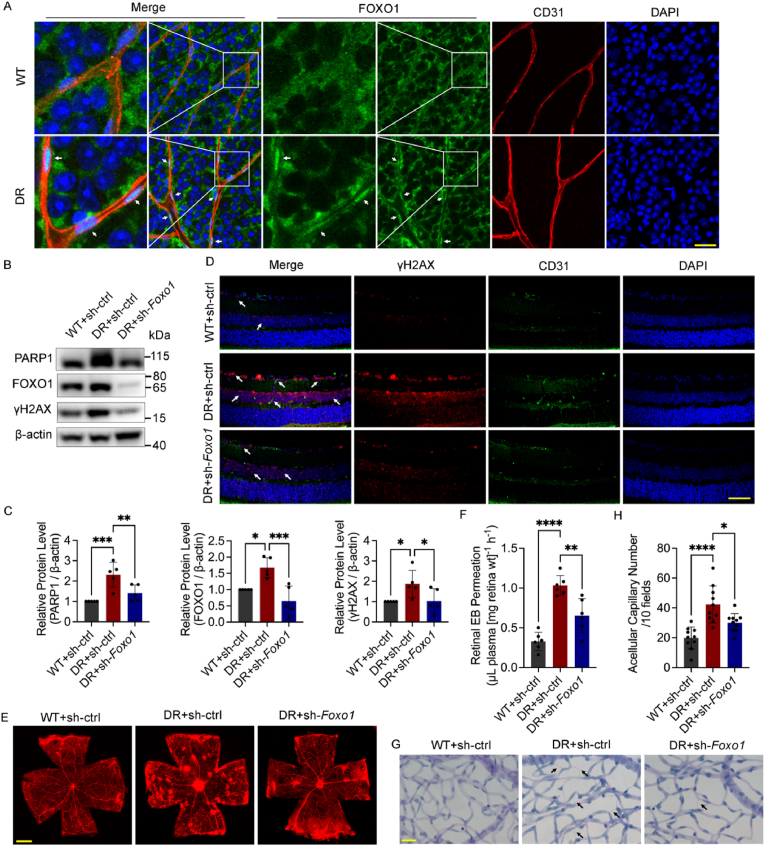
Fig. 1.
Foxo1 knockdown attenuates oxidative stress damage in diabetic mouse retina. A The localization of FOXO1 in the retina of nondiabetic C57BL/6 mice (WT) and diabetic mice (DR). White arrows indicate the nuclear translocation of FOXO1. n = 12. Scale bar, 100 μm. B and C Western blot analysis of PARP1, FOXO1 and γH2AX in the whole retina extracts. WT and DR mice received the intravitreal injection of adenovirus (Ads) for Foxo1 knockdown (sh-Foxo1), or vehicle controls (sh-ctrl) as indicated. n = 10. D Immunofluorescence staining of γH2AX. White arrows indicate γH2AX foci. n = 12. Scale bar, 50 μm. E and F Retinal vascular leakage assessed by Evans blue (EB) dye. The confocal analysis of whole-mounted retinas (E, scale bar: 500 μm) and statistical results of spectrophotometrically measured EB extravasation (F) are shown. n = 12. G and H The number of acellular capillaries. Scale bar, 20 μm. n = 10. Black arrows indicate acellular capillaries. All results are displayed as means ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA analysis. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)