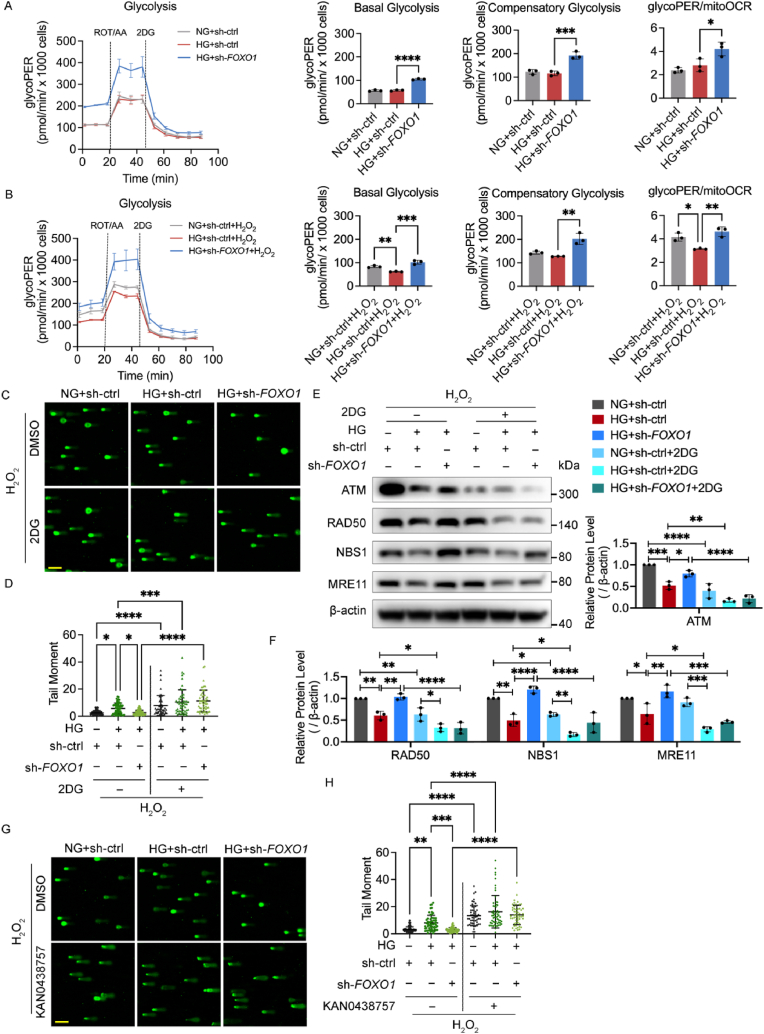
Fig. 5.
FOXO1 knockdown enhances DNA repair mediated by the MRN-ATM pathway in a glycolysis-dependent manner. A and B Glycolysis detected by Glycolysis Rate Kit. After being infected with sh-FOXO1 or sh-ctrl and then cultured in NG or HG for 48 h, HUVECs were subjected to H2O2 (B, 300 μM for 30 min, 2 h recovery), or left untreated (A). The ECAR and OCR were measured sequentially under basal conditions, following treatments of ROT/AA (0.5 μM) and 2-deoxy-glucose (2DG, 50 mM), and converted as glycolytic proton efflux rate (glycoPER) and mitochondrial oxygen consumption rate (mitoOCR). GlycoPER profiles, changes in basal glycolysis, compensatory glycolysis and glycoPER/mitoOCR are shown as indicated. C and D DNA damage levels assessed using comet assay. After being infected with sh-FOXO1 or sh-ctrl, HUVECs were treated with DMSO or 50 mM of 2DG in NG or HG for 48 h, and then subjected to H2O2 (300 μM for 30 min, 2 h recovery). The representative images (C, scale bar: 100 μm) and the scatter dot plot of the tail moment per cell (D) are shown. E and F Western blot analysis of ATM and MRN. HUVECs were treated in the same conditions as (C) and (D). G and H DNA damage levels were assessed using comet assay. After being infected with sh-FOXO1 or sh-ctrl, HUVECs were treated with DMSO or 25 μM of KAN0438757 in NG or HG for 48 h, and then subjected to H2O2 (300 μM for 30 min, 2 h recovery). The representative images (G, scale bar: 100 μm) and the scatter dot plot of the tail moment per cell (H) are shown. Each experiment was repeated independently at least three times. All results are displayed as means ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA analysis.