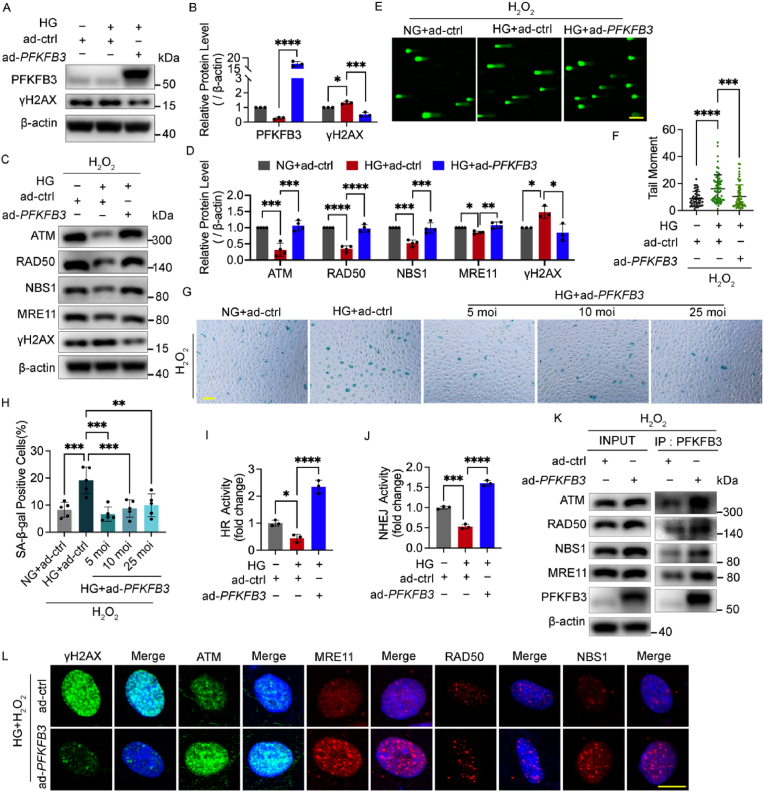
Fig. 7.
PFKFB3 overexpression restored impaired DNA repair in response to oxidative stress under high glucose by interaction with the MRN-ATM pathway. A and B Western blotting analysis of PFKFB3 and γH2AX. HUVECs were treated with Ads for PFKFB3 overexpression (ad-PFKFB3) or vehicle control (ad-ctrl) and then cultured in NG or HG for 48 h. C and D Western blotting analysis of ATM and MRN. After being infected with ad-PFKFB3 or ad-ctrl and then cultured in NG or HG for 48 h, HUVECs were subjected to H2O2 (300 μM for 30 min, 2 h recovery). E and F DNA damage levels assessed by comet assay. HUVECs were treated in the same conditions as (C) and (D). The representative images (E, scale bar: 100 μm) and the scatter dot plot of the tail moment per cell (F) are shown. G and H Cellular senescence detected by SA‐β‐Gal staining. After being treated with H2O2 (700 μM for 30 min), HUVECs were infected with Ads and then cultured in NG or HG for 48 h. Scale bar, 100 μm. I and J HR and NHEJ activity. After being treated with DNA repair reporter (DRR) assay, HUVECs were infected with Ads and then cultured in NG or HG for 48 h. K HUVECs were treated with ad-PFKFB3 or ad-ctrl for 48 h as indicated, and then subjected to H2O2 (300 μM for 30 min, 2 h recovery). Cell lysates (left, INPUT) and immunoprecipitated PFKFB3 (right, IP: PFKFB3) was immunoblotted with ATM and MRN antibody. L Confocal analysis of γH2AX, ATM and MRN foci. After being infected with ad-PFKFB3 or ad-ctrl and then cultured in HG for 48 h, HUVECs were subjected to H2O2 (300 μM for 30 min, 2 h recovery). Scale bar, 10 μm. Each experiment was repeated independently at least three times. All results are displayed as means ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA analysis.