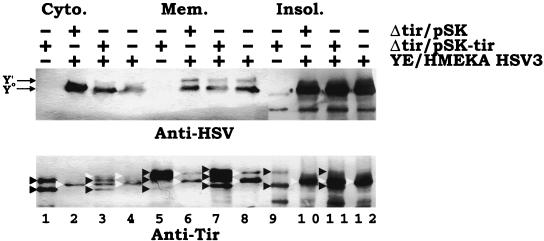
FIG. 7.
Dual EPEC-Yersinia infections do not lead to the further modification of the Yersinia-delivered TirHSV molecule. HeLa cells were left uninfected or infected with EPEC Δtir carrying pSK or pSK-tir (orf19 tir cesT) for 3 h. Monolayers were washed, and the presence of adherent EPEC colonies was confirmed by phase-contrast microscopy. Cells were then infected (MOI, 100:1) with YPIII/pIB29MEKA (YE/HMEKA) carrying pSK-HSV3 (orf19 tirHSV cesT) for a further 3 h before fractionating into saponin-released cytoplasmic (Cyto.), Triton-soluble membrane (Mem.), and insoluble (Insol.) fractions. Samples were processed for Western analysis (SDS-PAGE [6% polyacrylamide]) and probed with anti-HSV (top panel) or anti-Tir (bottom panel) antibodies. + and − indicates the presence and absence of the strain during infection, respectively. In the top panel, arrows indicate the position of the Yersinia-delivered Y0 and Y′ TirHSV species. Note the absence of an additional band corresponding to the Y" form. In the bottom panel, black arrowheads indicate the position of EPEC-delivered Tir species, with white arrowheads indicating the position of Yersinia-delivered TirHSV species. EPEC-delivered Tir species are lacking the HSV epitope and thus display a smaller apparent molecular mass than the corresponding Yersinia delivered species. Lanes are numbered sequentially.