Fig. 3: A Framework for Successful IO-based Treatment in PDAC.
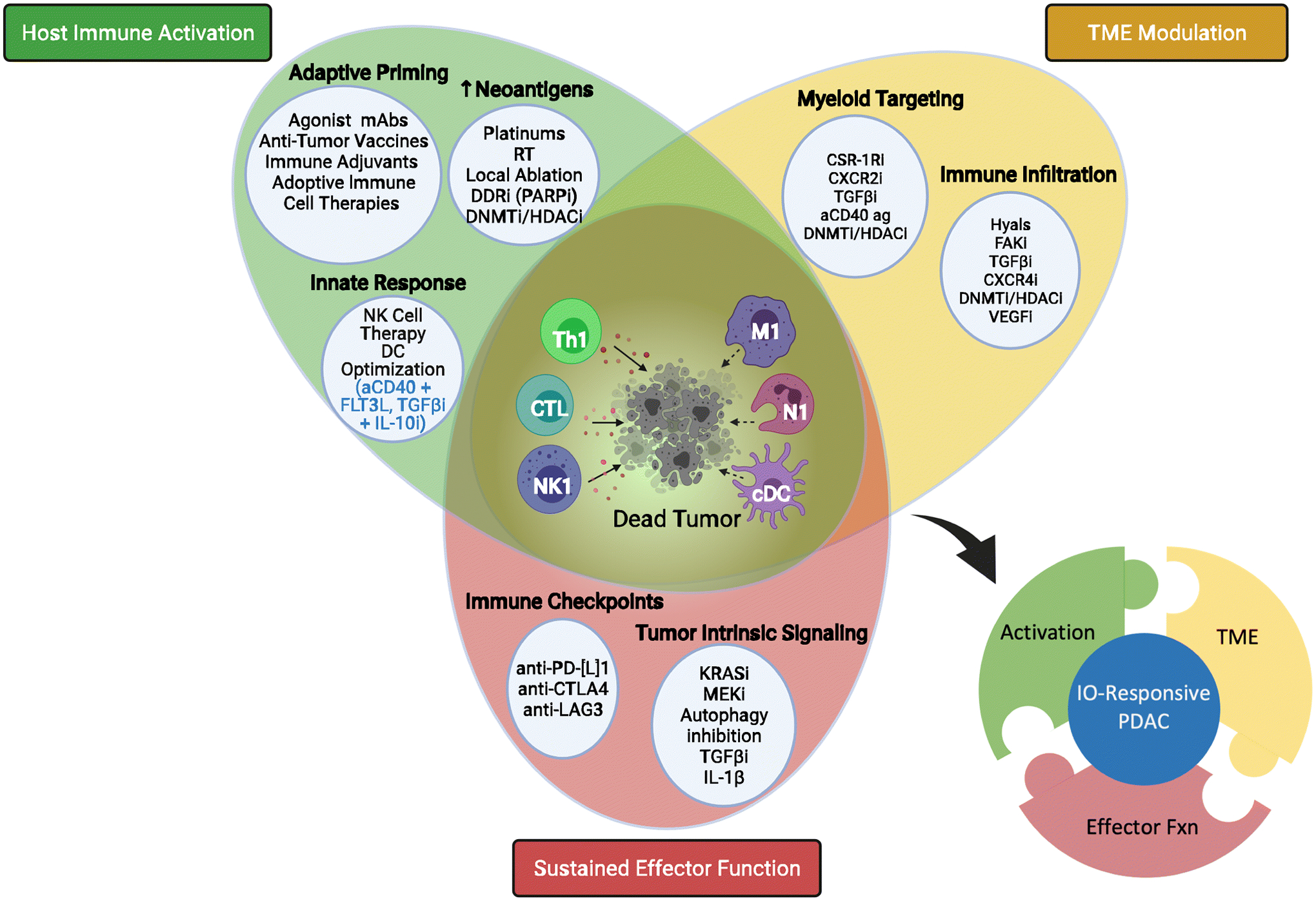
To block immune escape, next generation IO-based approaches for PDAC must be built on targeting immune priming/activation pathways simultaneously with modulating local TME immunosuppression and blocking immune checkpoints blockade for effective sustained anti-tumor immune trafficking and sustained cytotoxic response. This will require several IO and targeted agents on top of conventional therapies. Standard chemotherapy with combinatorial cocktail of an anti-tumor vaccine, co-stimulatory agent (aCD40), TME crosstalk modulator (CXC4Ri or TGFβ trap), and ICB (aPD-1) is one such potential combination. Key (selected terms): [cDC] conventional dendritic cell; [CSF-1Ri] colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor inhibitor; [CTL] cytotoxic T lymphocyte; [CTLA-4] cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4; [DDRi] DNA damage repair inhibitor; [DNMTi] DNA methyltransferase inhibitor; [FAKi] focal adhesion kinase inhibitor; [FLT3L] Fms-related receptor tyrosine kinase 3; [HDACi] histone deacetylase inhibitor; [Hyals] hyalanurinases; [LAG3] lymphocyte activating 3; [M1] tumor associated macrophage, type I phenotype; [mAbs] monoclonal antibodies; [N1] Neutrophil, type 1 phenotype; [NK] – natural killer; [NK1] natural killer cell, type 1 phenotype; [PARPi] Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor; [PD-L1] – programmed death-ligand 1; [RT] radiation therapy; [TGFβ] transforming growth factor beta; [Th1] T helper cell, type 1 phenotype; [VEGFi] Vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor. Created with BioRender.com.
