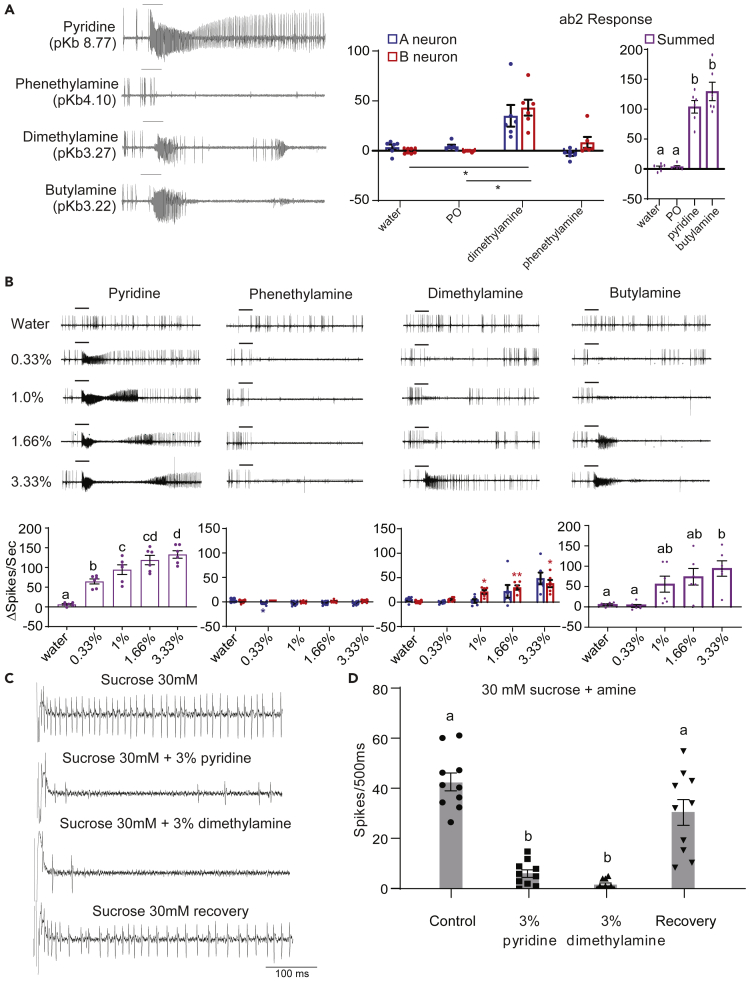
Figure 4.
Response to amines in the olfactory and gustatory system
(A) Representative traces (left) and mean responses from A and B neurons (middle) or summation of responses obtained from A and B neurons for a 1-s period of stimulation from the indicated compounds. For water, PO, dimethylamine and phenethylamine (middle) blue bars indicate responses from A neurons while red bars indicate responses from the B neurons. In the right figure all bars represent summation of responses obtained from both A and B types for water, PO, pyridine and butylamine. For the rightmost figure, the values shown for water and PO are actual sums of responses from A and B neurons in the middle figure. Each count was begun at the start of the increase in spike frequency. All compounds tested at 3.33% concentration in water, except phenethylamine which was dissolved in paraffin oil. All recordings were obtained from 3–5 days old wildtype (CS) flies. n = 4–6 sensilla from 6 flies. Error bars indicate SEM Dots indicate individual data points. Repeated measures 1-way ANOVA with Geisser-Greenhouse correction (between responses from same neuron from the middle figure) followed by Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons. ∗∗p < 0.01. In the rightmost figure, lower case alphabets indicate statistically different groups.
(B) Representative traces (top) and mean responses (bottom) for a 1-s period of stimulation from each concentration of the four basic compounds. Each count was begun at the start of the increase in spike frequency. For dimethylamine and phenethylamine, blue and red bars indicate responses obtained from (A and B) neurons respectively. For pyridine and butylamine, bars indicate summed responses from both neuron types. All compounds were dissolved in water, except phenethylamine which was dissolved in paraffin oil. All recordings were obtained from 3–5 days old wildtype (CS) flies. n = 6 sensilla from 6 flies. Error bars indicate SEM Dots indicate individual data points. Repeated measures 1-way ANOVA with Geisser-Greenhouse (between responses from same neuron type for dimethylamine and phenethylamine) correction followed by Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons. For phenethylamine and dimethyamine, blue and red asterisks indicate statistically significant difference from the response obtained with PO from the A neurons and the B neurons respectively. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01. For pyridine and butylamine, small case alphabets indicate statistically different groups.
(C) Representative traces for the first 500 ms recorded when labellar L-type sensilla are stimulated with the mentioned tastants. All recordings were obtained from 5–7 days old wild type (CS) flies.
(D) Mean responses along with individual data points for the first 500msecs recorded when labellar L-type sensilla are stimulated with the mentioned tastants. All recordings were obtained from 5–7 days old wild type (CS) flies. n = 10 sensilla from 3 flies. Error bars indicate SEM Paired 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test for pairwise comparison. Lower case alphabets indicate statistically different groups.