FIGURE 1.
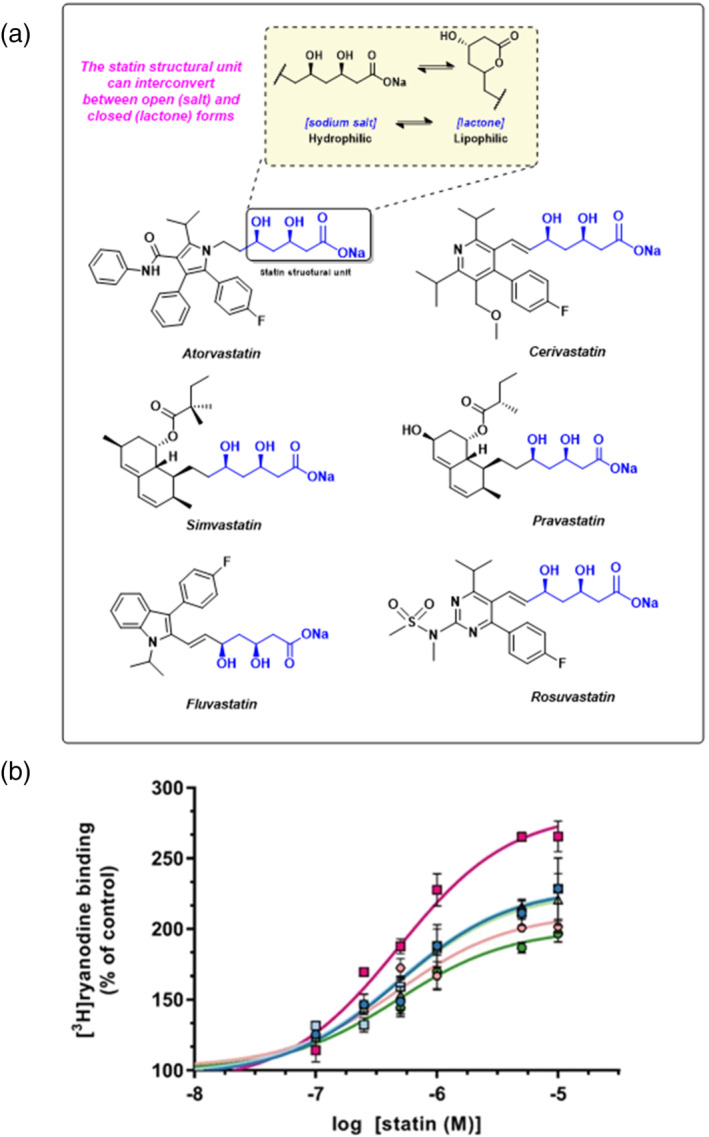
The effects of commonly prescribed statins on ryanodine RyR1 channel activity. (a) The chemical structures of atorvastatin, cervistatin, simvastatin, pravastatin, fluvastatin and rosuvastatin are shown. In each structure, the essential statin structural unit required for activity at HMG‐CoA reductase is indicated in blue. This unit can exist in both an open and ring‐closed form as illustrated in the inset. (b) Increase of [3H]ryanodine binding to sheep skeletal muscle SR membrane vesicles by commonly prescribed statins indicated as a percentage of control binding levels (10 μM Ca2+ as sole activator). Atorvastatin ( ; EC50 = 0.76 μM, Emax = 229%) cerivastatin (
; EC50 = 0.76 μM, Emax = 229%) cerivastatin ( ; EC50 = 0.42 μM, Emax = 283%), simvastatin (
; EC50 = 0.42 μM, Emax = 283%), simvastatin ( ; EC50 = 0.70 μM, Emax = 230%), pravastatin (
; EC50 = 0.70 μM, Emax = 230%), pravastatin ( ; EC50 = 0.44 μM, max = 227%), fluvastatin (
; EC50 = 0.44 μM, max = 227%), fluvastatin ( ; EC50 = 0.42, Emax = 211%) and rosuvastatin (
; EC50 = 0.42, Emax = 211%) and rosuvastatin ( ; EC50 = 0.49 μM, Emax = 200%) are shown. Mean ± SEM; n = 5; where error bars are not visible, they are within the symbol
; EC50 = 0.49 μM, Emax = 200%) are shown. Mean ± SEM; n = 5; where error bars are not visible, they are within the symbol
