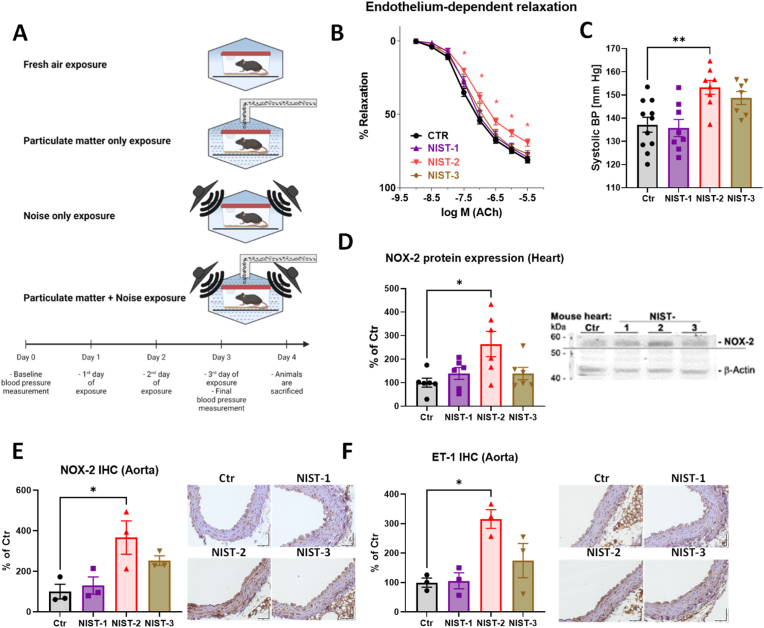
Fig. 1.
Mouse exposure protocol and testing of different preparations of fine particulate matter (NIST PM). Timeline and schematic illustration of the exposure protocol for both PM and noise (A). The vascular function was measured in isolated aortic rings (B). The endothelium-dependent relaxation in presence of acetylcholine (ACh) was significantly impaired for the NIST2 PM preparation, but not for the other NIST preparations. The endothelium-independent relaxation in presence of nitro-glycerine (GTN) was not changed after the exposure to any of the NIST PM preparations. The blood pressure of the exposed mice was measured by the non-invasive tail cuff method (C). Systolic blood pressure was significantly increased for the NIST2 PM preparation, but not for other preparations, although NIST3 showed an increase by trend. The Western blot (WB) of the heart tissue proteins, showed a significant increase of NOX-2 in the NIST2 group, but not in the other NIST PM preparation groups (D). Representative original blots are shown besides the quantification. Immunohistochemical staining revealed that NOX-2 and endothelin-1 protein was also significantly upregulated by PM (NIST2) exposure, whereas only a minor trend of increase was seen with NIST3 and no effect was observed with NIST1. Representative immunohistochemical staining images are shown besides the quantification. Data are presented as mean ± SEM and individual values are shown where possible. The statistics was performed from n = 11–19 (B), 7–11 (C), 6 (D), 3 (E,F) independent experiments. The statistical significance of p < 0.05 is represented with an asterisk (*).