Figure 1.
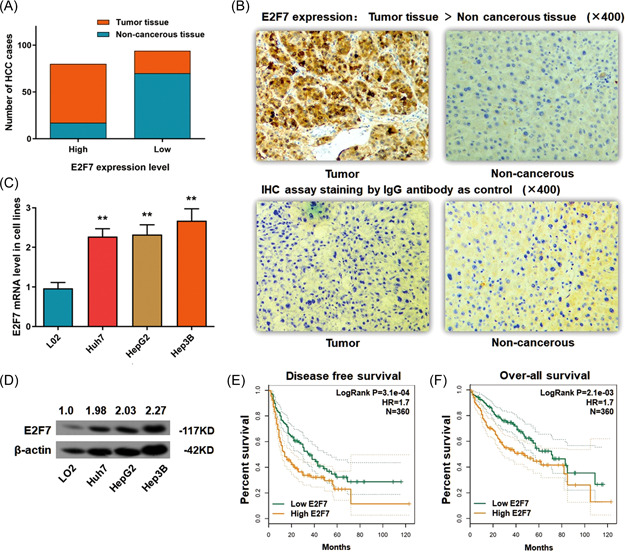
E2F7 ascends in HCC tumor tissues and cell lines. (A) Statistic of the number of cases with higher or lower expression of E2F7 in HCC specimens. E2F7 ascended in most of the tumor tissues (63/87) and was expressed at a lower level in most of the adjacent noncancerous tissues (17/87) (p < 0.01). (B) Representative graph of immunohistochemistry analysis (400×) of the HCC cases. The IgG antibody was used for staining the specimens as a control. E2F7 expression in tumor specimens was significantly higher than in adjacent noncancerous tissues. (C) RT‐qPCR assay demonstrated a significantly high expression of E2F7 mRNA in three HCC cell lines, in comparison with the control L02 cells (**p < 0.01). (D) The Western blot analysis demonstrated a remarkable raising of E2F7 protein in three HCC cell lines, in comparison with the control L02 cells (p < 0.01). (E) Disease‐free survival (DFS) analysis according to HCC patients' follow‐up information was presented by the Kaplan–Meier plot. High Anillin expression in HCC tissue is correlated with poor overall survival (OS) (360 cases, p = 3.1e−04). (F) OS analysis according to HCC patients' follow‐up information was presented by the Kaplan–Meier plot. High Anillin expression in HCC tissue is correlated with poor OS (360 cases, p = 2.1e−05). HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; mRNA, messenger RNA; RT‐qPCR, real‐time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
