Figure 5.
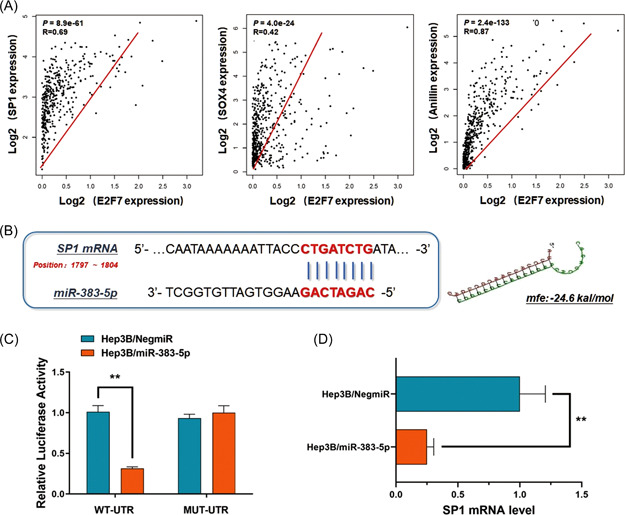
MicroRNA‐383‐5p negatively regulates SP1 mRNA level in a posttranscriptional way, and potentially correlated with E2F7. (A) According to the analysis of the TCGA liver cancer data set (n = 361), E2F7 was highly expressed in HCC cells, and presented a positive correlation with SP1 (p = 8.9e−61, R = 0.69), SOX4 (P = 4.0e−24, R = 0.42), and Anillin (p = 2.4e−133, R = 0.87), prompting some regulation mechanisms between E2F7 and SP1/SOX4/Anillin axis. (B) MiR‐383‐5p was a potential upstream regulator of SP1 in Hep3B cells by directly interacting with the 3′‐UTR of SP1 mRNA. The minimum free energy (Mfe) hybridization is calculated with significance as −24.6 kal/mol. (C) A direct interaction was detected between SP1 mRNA and miR‐383‐5p via a Dual‐luciferase reporter assay. Ectopic expression of miR‐383‐5p in Hep3B cells (Hep3B/miR‐383‐5p) significantly declined the luciferase signal of wildtype binding sequence compared with the negative control (Hep3B/NigmiR). The signal suppression induced by miR‐383‐5p defected in Hep3B cells transfected with the mutated binding sequence (**p < 0.01). (D) RT‐qPCR assay indicated a significant decrease of SP1 mRNA level in Hep3B cells, transfected with miR‐383‐5p mimics (**p < 0.01). HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; mRNA, messenger RNA; RT‐qPCR, real‐time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; TCGA, the Cancer Genome Altas. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
