Figure 6.
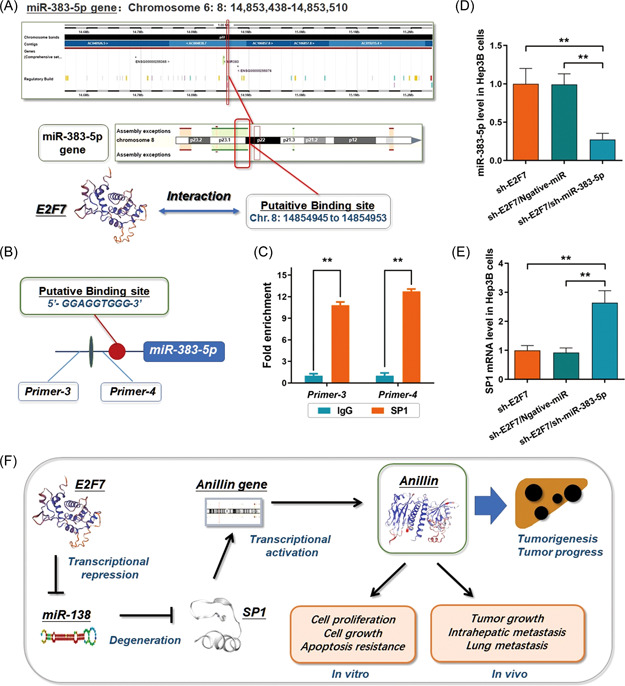
E2F7 transcriptionally targets miR‐383‐5p and modulates the SP1/SOX4/Anillin axis. (A) E2F7 was predicted as a transcription factor that binds to the upstream miR‐383‐5p gene (5′‐GGAGGTGGG‐3′, Chr. 8: 14854945 to 14854953, P = 2.89e‐05). (B) and (C) ChIP assay was carried out for investigating the direct interaction between E2F7 and the putative promoter region upstream miR‐383‐5p gene (**p < 0.01). IgG was used for the negative control. (D) MiR‐383‐5p presented a relatively higher level in the E2F7 depleted Hep3B cells. And this high expression of miR‐383‐5p was significantly through the shRNA method (**p < 0.01). (E) By suppressing miR‐383‐5p, the downregulation of SP1 mRNA induced by E2F7 depletion was significantly rescued (**p < 0.01). (F) Summary of the regulation of E277 on the axis of SP1/SOX4/Anillin by negatively modulating the transcription of miR‐383‐5p, which sequentially facilitates HCC tumor growth. HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; mRNA, messenger RNA. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
