FIG 1.
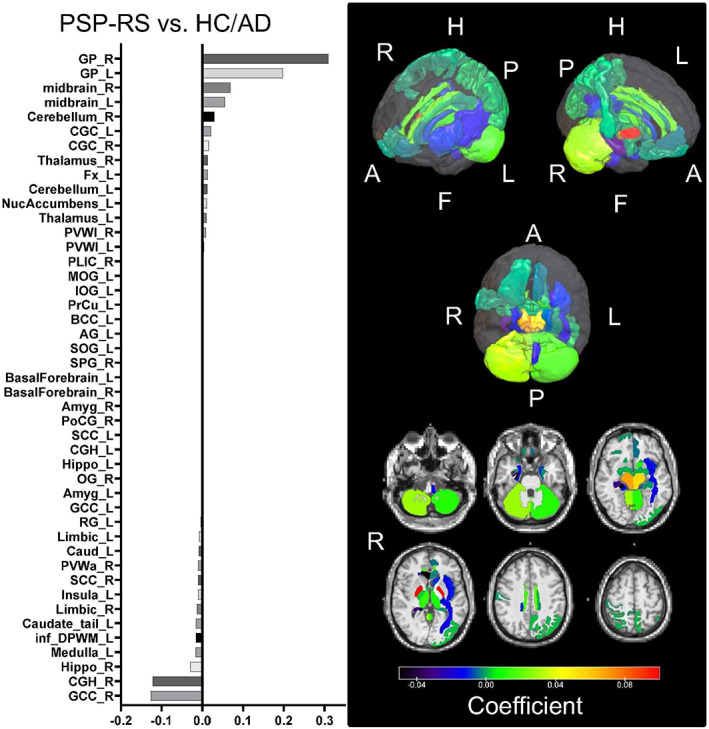
Weighting coefficients for the ROIs that contributed most to the discrimination between the PSP‐RS and AD + HC groups. The bar chart on the left shows the important ROIs from the top in the order of positive to negative weighting coefficients. In the right panel, the upper panel shows the weighting coefficients assigned to the ROIs in the three‐dimensional brain, and the lower panel shows the axial cross‐section of the ROIs, with the GP and midbrain having higher weighting coefficients, from red to yellow. A, Anterior; AD, Alzheimer's disease; AG, angular gyrus; Amyg, amygdala; BCC, body of corpus callosum; Caud, caudate nucleus; CGC, cingulum (cingulate gyrus); CGH, cingulum (hippocampus gyrus); F, foot; Fx, fornix (column and body of fornix); GCC, genu of corpus callosum; GP, globus pallidus; H, head; HC, healthy control; Hippo, hippocampus; inf_DPWM, inferior deep white matter; IOG, inferior occipital gyrus; L, left; MOG, middle occipital gyrus; NucAccumbens, nucleus accumbens; OG, orbital gyrus; P, posterior; PLIC, posterior limb of internal capsule; PoCG, postcentral gyrus; PrCu, pre‐cuneus; PSP‐RS, progressive supranuclear palsy–Richardson syndrome; PVWa, periventricular white matter anterior; PVWl, periventricular white matter lateral; R, right; RG, gyrus rectus; ROI, region of interest; SCC, splenium of corpus callosum; SOG, superior occipital gyrus; SPG, superior parietal gyrus. See also Table S1 for the abbreviations in the left graph. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
