FIGURE 3.
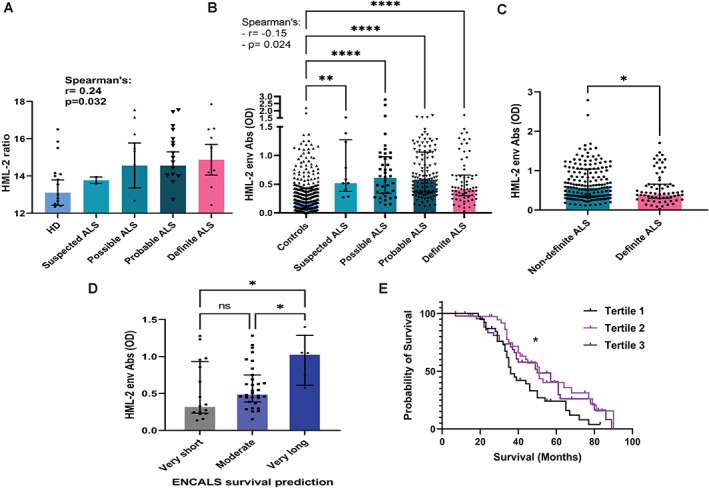
Correlation of HML‐2 ratio and antibodies with severity of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). (A) HML‐2 ratio in individuals with ALS classified by El Escorial criteria (suspected: n = 2; possible: n = 13; probable: n = 29 and definite: n = 11) and in healthy donors (HD) (n = 27) as measured by digital polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Correlation analysis by Spearman's r test (r = 0.24; p = 0.03). (B) Levels of HML‐2 env antibodies in individuals with ALS classified by El Escorial criteria (suspected: n = 10; possible: n = 39; probable: n = 112 and definite: n = 67) and in controls (n = 327; 242 HD and 85 multiple sclerosis [MS]), as determined by peptide enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Comparison between groups (Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn post‐hoc analysis). Correlation analysis by Spearman r test (r = −0.15; p = 0.02). (C) Levels of HML‐2 env antibodies in individuals with non‐definite and definite ALS according to El Escorial criteria (unpaired t‐test; p = 0.03). (D) Levels of HML‐2 env antibodies in ALS individuals grouped by predicted survival according to the ENCALS model (analysis of variance [ANOVA] with Sidak post‐hoc test; p = 0.02 and p = 0.03). (E) Analysis of observed survival in individuals with ALS according to the levels of antibodies to a select HML‐2 env peptide. HML‐2 antibodies optical density (ODs): Tertile 1 (n = 78); OD: 0.026–0.380; Tertile 2 (n = 78); OD: 0.381–0.749; Tertile 3 (n = 79); OD: 0.750–2.79. Log‐rank Mantel–Cox test; p = 0.03. [Color figure can be viewed at www.annalsofneurology.org]
