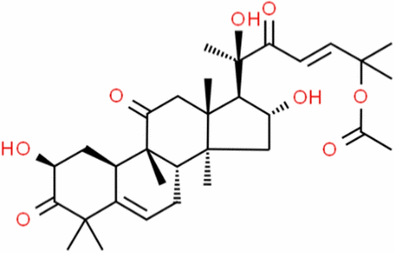
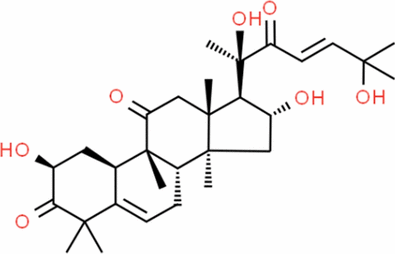
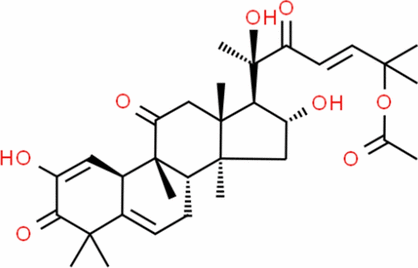
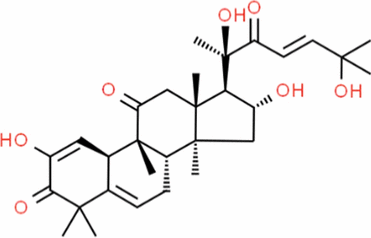
Table 2.
The anticancer mechanisms of cucurbitacins tested in vitro and in vivo experimental cancer models
| Tested cucurbitacin | Experimental model | Anticancer mechanisms | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cucurbitacin B
|
In vitro Melanoma cells A375 |
↓proliferation ↓MAPK |
[79] |
|
In vivo Mice NOD-SCID xenograft melanoma model |
↑ cytotoxicity ↓tumour growth |
||
|
In vitro Gastric cancer cells SGC7901/DDP |
Reversed multi-drug resistance ↓HIF-1a, ↓P-gp ↑apoptosis, ↑autophagy ↓CIP2A/PP2A/mTORC1, ↓mTORC1, ↓PP2A |
[80] | |
|
In vitro Hepatoma human cells HepG2, BEL-7402 |
↓cell invasion, ↓migration ↓MMP-9,↓ ERK 1/2,↓ p38, ↓Akt |
[81] | |
|
In vitro Non-small cells lung cancer (NSLC) H1299 |
↑epigenetic modifications ↓histone deacetylase ↓DNA methyltransferase ↑tumour suppressor genes: ↑CDKN1A, ↑CDKN2A ↓oncogenes ↓β-catenin, ↓Wnt3, ↓Wnt3a |
[82, 83] | |
|
In vivo Mice Lung tumourigenesis model |
↓angiogenesis | ||
|
In vitro Human cholangiocarcinoma cells KKU-100 |
Antiproliferative Cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase ↓cyclin A, cyclin D1 ↑p21, ↑p53, ↓FAK, ↓EGFR, ↓HER2 ↓FAK/PI3K/PDK1/AKT, FAK/p53 |
[84] | |
|
In vitro Breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231, SKBR3- MCF-7, 4T-1 |
↓ cells growth ↓HER2, ↓EGFR, ↓ILK1/ YB-1/Twist ↓ITGA6, ↓ITGB4 |
[85] | |
|
In vivo Mice MDA-MB-231 athymic nude model |
↓tumour volume | ||
|
In vitro Breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231 cells |
↑apoptosis, ↑morphologic changes ↑irregular polymerization of the microtubule ↑arrest at the G2/M cell cycle phase ↓c-Myc, ↓nucleophosmin/B23 |
[86] | |
|
In vitro Breast cancer cells MDA‐MB‐231, SKBR‐3 |
↓cell migration ↓RAC1/CDC42/RhoA ↓FAK, ↓RAC1, ↓CDC42 |
[87] | |
|
In vivo Mice BALB/c nude bearing SKBR‐3 cells |
↓metastasis | ||
|
In vitro Prostate cancer cells LNCaP, PC-3 |
↑apoptosis ↑Caspase 3, ↑ Caspase 7 ↑Sub-G0/G1 phase |
[88] | |
|
In vivo Mice PC-3 xenograft growth model |
↓ATP citrate lyase (ACLY) | ||
|
In vitro Human glioblastoma cells line U87 |
↓angiogenesis ↓α5β1 |
[69] | |
|
Cucurbitacin D
|
In vitro Cervical cancer cells CaSki, SiHa |
↓tumor cells growth, ↓metastasis ↑annexin V, ↑ PARP ↑cell cycle arrest at the G1/S phase ↑CDK4, ↑cyclin D1 ↓RB protein phosphorylation ↓PI3K/AKT, ↓STAT3, ↓MMP9, ↓c-Myc |
[70] |
|
In vivo Athymic nude mice bearing CaSki cells |
↓ tumour growth | ||
|
In vitro Pancreatic cancer cells AsPC-1, Capan-1 |
↑apoptosis ↑cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase ↑ROS, ↑p38, ↑c-Jun, ↑ROS/p38 ↓cyclin B1, ↓PARP ↓phospho-cdc2, ↓phospho-cdc25c ↑p21, ↓cyclin/CDK ↑caspases 7, ↑caspase 8 |
[91] | |
|
In vitro Non-small cells lung cancer NSCLC-N6 cells |
cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase ↑CDK1 mRNA ↓p53 |
[72] | |
|
Cucurbitacin E
|
In vitro Glioblastoma cells GBM8401, U-87-MG |
↓cell proliferation, ↑apoptosis ↑ G2/M phase of the cell cycle ↓mitosis, ↓CDC2, ↓cyclin B1 ↓GADD45β, ↓CDC2/cyclin B1 |
[73] |
|
In vitro A549 non-small cells lung cancer NSCLC cells lung cancer cells |
↑apoptosis ↑EGFR, ↑EGFR/MAPK, ↑ERK1/2, ↓MEK1/2 ↑caspases -3, ↑caspase -9, ↓survivin, ↓STAT3 ↓cyclinA2, ↓cyclinB1, ↓cyclin E1 ↑G1/G0 phase of the cell cycle |
[74] | |
|
In vitro GBM8401malignant glioma cells GBM8401 |
antiproliferative, ↓cell growth ↑cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase ↑GADD45γ, ↓B1/CDC2 |
[75] | |
|
Cucurbitacin I
|
In vitro SKOV3 ovarian cancer cells PANC-1 pancreatic cancers cells |
↑apoptosis, ↑ autophagy ↑ERS, ↑IRE1α, ↑PERK, ↑caspase-12 ↑CHOP, ↑Bax |
[76] |
|
In vitro colon cancer cells SW480 |
↓cell viability, ↑apoptosis, ↓proliferation ↑cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase ↓cyclin A, ↓cyclin B1, ↓CDC25C, ↓CDK1 ↓ CDK1/cyclin B1, ↓caspases -3, -7, -8, -9 |
[77] | |
|
In vivo Mice Syngeneic transplanted CT-26 BALB/c |
↓tumour growth ↓proliferation |
||
|
Cucurbitacin II
|
In vitro Non-small cells lung cancer NSCLC lung cancer cells A549 |
↑apoptosis, ↑cell cycle arrest ↓EGFR, ↓EGFR/MAPK, ↓cyclinB1, ↓ERK1, ↓MEK1, ↓MEK2, ↑survivin, ↑BRAF, ↑Raf1, ↑ERK2, ↑STAT3, ↓ERK1, ↓MEK1 |
[78] |
|
↑apoptosis, ↓STAT3 ↑G2/M phase cell cycle arrest, ↓EGFR/MAPK |
[79] | ||
|
↓cell growth, ↑apoptosis ↓ STAT3, ↓EGFR |
[80] |
↑ increase; ↓decrease; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; HIF-1a: hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; P-gp: P-glycoprotein; CIP2A: cellular inhibitor of PP2A; PP2A: protein phosphatase 2; mTORC1: mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; MMP-9: matrix metallopeptidase 9; ERK 1/2: extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2; p38: group of MAPK; Akt: protein kinase B; CDKN1A: cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1A; CDKN2A: cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2A; Wnt3: proto-oncogene family member 3; Wnt3a: proto-oncogene family member 3a; p21: cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor; p53: tumor suppressor gene; FAK: focal adhesion kinase; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; HER2: human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PDK1: 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1; ILK1: integrin-linked kinase 1; YB-1: Y-box binding protein; Twist: helix-loop-helix transcription factor; ITGA6: integrin subunit alpha 6; ITGB4: integrin subunit beta 4; c-Myc: multifunctional transcription factor; nucleophosmin/B23: multifunctional nucleolar protein; RAC1: Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1; CDC42: cell division control protein 42; RhoA: Ras homolog family member A; ACYL: ATP citrate lyase; α5β1: alpha 5 beta 1 protein; PARP: poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases; CDK4: cyclin dependent kinase 4; RB: retinoblastoma protein; STAT3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; ROS: reactive oxygen species; c-Jun: transcription factor Jun; phospho-cdc2: phosphorylated cell division cycle 2; phospho-cdc25c: phosphorylated protein that regulates cell division; CDK1: cyclin dependent kinase 1; GADD45β: growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible 45 beta; MEK1/2: mitogen activated protein kinase kinases 1 and 2; GADD45γ: growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible 45 gamma; B1/CDC2: cyclin B1-dependet Cdc2 kinase; ERS: endoplasmic reticulum stress; IRE1α: inositol-requiring transmembrane kinase endoribonuclease 1 alpha; PERK: endoplasmic reticulum kinase; CHOP: DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein; Bax: bcl-2-like protein 4; CDC25C: cell division control protein 25C; survivin: member of the inhibitor of apoptosis gene family; BRAF: B-Raf proto-oncogene; Raf1: Raf-1 proto-oncogene