Figure 3.
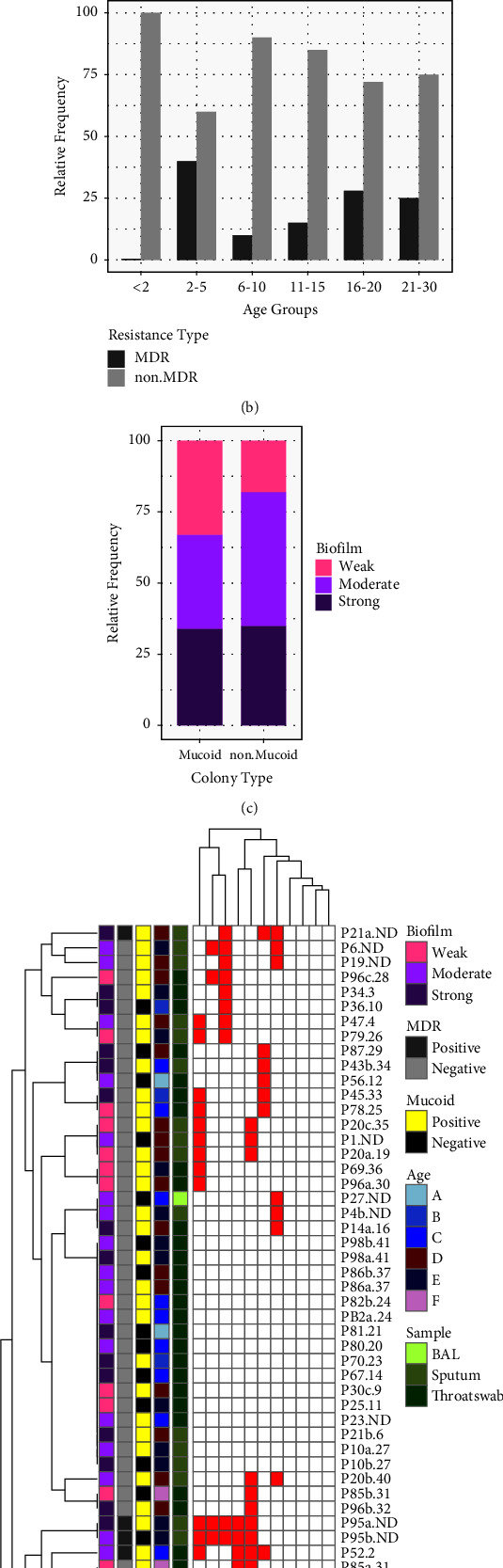
Population structure of P. aeruginosa isolates. (a) Relative frequency of resistance to antibiotics in P. aeruginosa isolates and biofilm formation status. (b) Relative frequency of MDR and non-MDRP. aeruginosa isolates vs. age group. (c) Relative frequency of mucoid/non mucoid phenotype of P. aeruginosa and biofilm formation status. (d) Overview of antimicrobial-resistance profiles and other characteristics of P. aeruginosa isolates. GM, gentamicin; CIP, ciprofloxacin; IMI, imipenem; CAZ, ceftazidime; MEM, meropenem; PTZ, piperacillin-tazobactam; CPM, cefepime; ATM, aztreonam; TN, tobramycin; AK, amikacin; LEV, levofloxacin; age group is represented as A < 2, B 2–5, C 6–10, D 11–15, E 16–20, F 20–30 years of age; (P) P. aeruginosa; a, b and c letters represent the different morphotypes of the same bacteria isolated from the same patient; red squares are representative of resistance and white squares represent susceptibility to the tested antibiotic.
