FIG 1. Pathophysiologic mechanisms of peripartum cardiomyopathy.
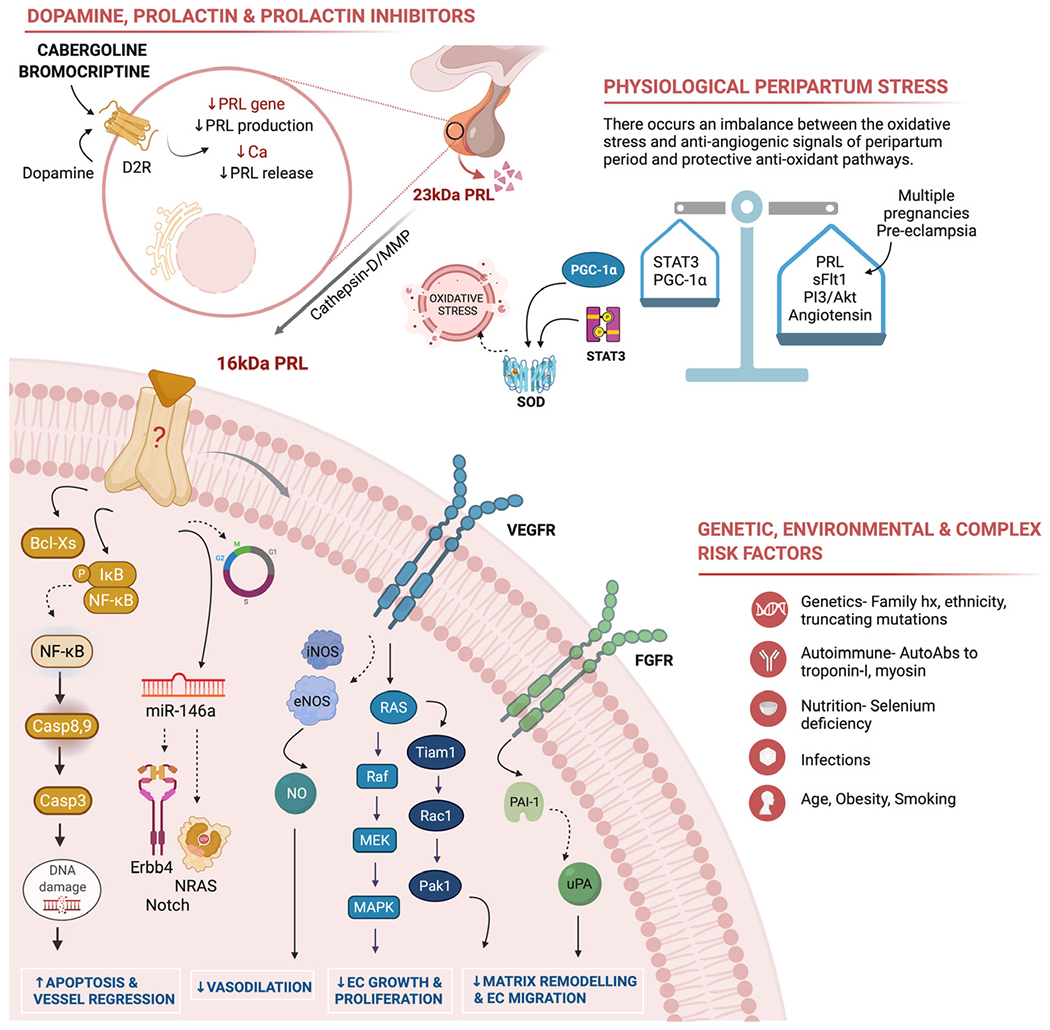
Top left panel – Bromocriptine acts on the G-protein coupled dopamine D2 receptor which in turn suppresses prolactin (PRL) gene expression, inhibits lactotroph proliferation61 and decreases PRL release from secretory granules. Inhibiting PRL release further inhibits 16kDa fragment generation by proteolytic enzymes. Top right panel — Cardiac angiogenic imbalance is caused by the oxidative stress and anti-angiogenic signals associated with the peripartum period [PRL, soluble FLT1 and angiotensin II] and protective antioxidant and angiogenic pathways [signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor c coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) and phosphoinositid-3-kinase (PI3) and protein kinase B (Akt)]. Bottom right panel – Other genetic, inflammatory, autoimmune, infectious, and environmental have been implicated in the development of PPCM. Bottom left circular panel – Demonstrates the anti-angiogenic mechanisms of 16kDa PRL fragment. i) Apoptosis and vessel regression: 16kDa PRL activates nuclear factor kappa B (NFkB) and Bcl-XS which initiates apoptotic pathways causing cell death. Cell cycle arrest is mediated through effect on cyclin D1, B1 and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Induction of microRNA-146a expression which affects endothelial cell proliferation through downregulation of NRAS (neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog) and Erb-B2 receptor tyrosine kinase 4 (Erbb4). ii) Inhibition of vasodilation: 16kDa PRL decreases NO (nitric oxide)-mediated vasodilation by blocking both eNOS (endothelial nitric oxide synthase) and iNOS (inducible nitric oxide synthase) expression. iii) Inhibition of endothelial cell (EC) growth and proliferation: 16kDa PRL prevents EC proliferation via inhibition of fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-mediated activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) [Ras/Raf/MEK/MAPK signal pathway]. iv) Inhibition of EC migration and vascular remodeling: 16kDa PRL decreases EC migration via downregulation of the Ras-Tiam1-Rac1-Pak1 signaling pathway and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1)-mediated inhibition of urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA).
