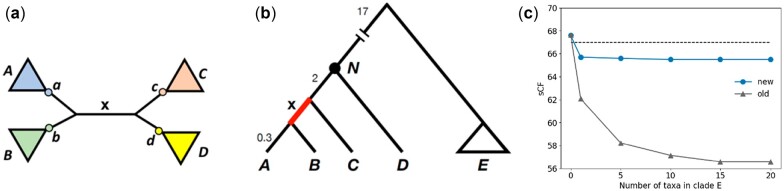
Fig. 1.
(a) A quartet will be sampled from states at internal nodes in the new sCF, but from tip taxa within clades in the old sCF. (b) The species tree used for simulation. sCFs are always calculated for branch x (highlighted in red), whose length is 0.7 in coalescent units. There is always one taxon in , while the number of taxa in clade is allowed to vary. Note that the tree is not to scale; branch lengths shown are in coalescent units. (c) Comparison of sCFs for branch x in panel (b) using two methods. The new method for calculating sCFs is less sensitive to sampling distant taxa as compared to the old version. The horizontal dashed line shows the expected level of gene tree concordance (A color version of this figure appears in the online version of this article)