Fig. 1.
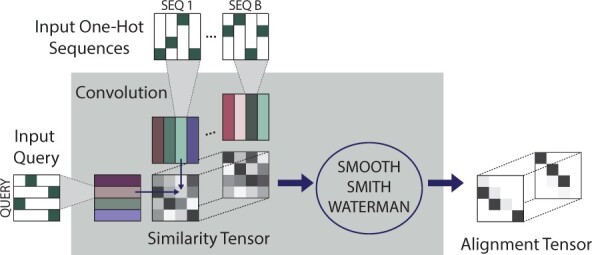
Learned alignment module (LAM). The residues of B sequences and a ‘query’ sequence are mapped to vectors using a convolution. For each sequence k, an alignment score matrix a is computed by taking the dot products of the vectors representing the query sequence and the vectors representing sequence k. The similarity tensor is formed by concatenating these matrices, and then our differentiable implementation of smooth Smith–Waterman is applied to each similarity matrix in the tensor to produce an alignment. The resulting B smooth pairwise alignments (all aligned to the query sequence) are illustrated as the ‘Alignment Tensor’
