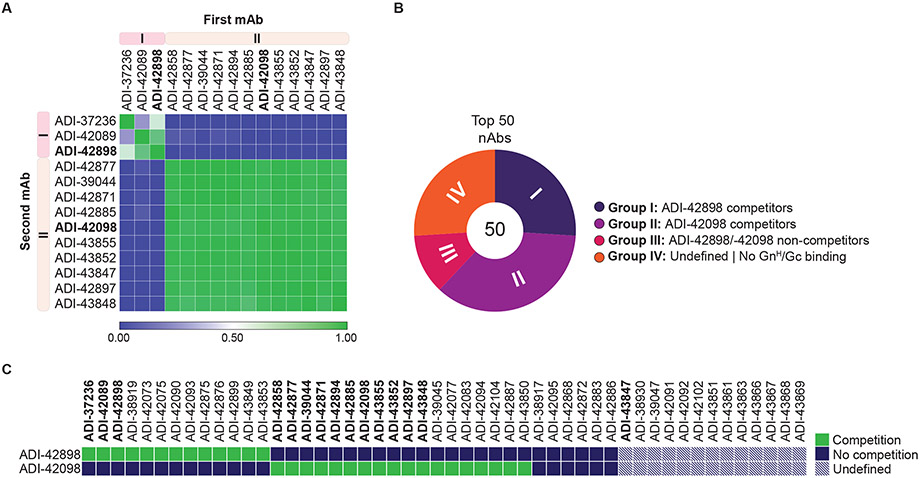
Fig. 3: Epitope binning of nAbs by competition analysis.
(A) Heatmap of competitive pairwise mAb binding studies to rVSV-PUUV-Gn/Gc. Percent mAb competition by the second mAb (columns) was normalized to the binding ELISA value for un-competed binding by the first mAb (rows). Antibodies were clustered according to their Pearson correlation-generated relatedness scores using Morpheus software (Broad Institute, Cambridge, USA). Averages (n=2-4) from one to two experiments. (B) Proportion of mAbs competing with ADI-42898 or ADI-42098 was determined in a high-throughput yeast competition assay by binding of IgG-displaying yeast cells to soluble PUUV GnH/Gc pre-complexed with F(ab)s of ADI-42898 or ADI-42098. Number in the center of the pie chart denotes the total number of mAbs analyzed. Each group (I-IV) is represented as a segment proportional to the group size. (C) Heatmap showing the capacity of selected mAbs to compete with ADI-42898 or ADI-42098 for binding to PUUV GnH/Gc from the experiments in panel B. mAbs marked in bold were tested in both competition-binding studies.