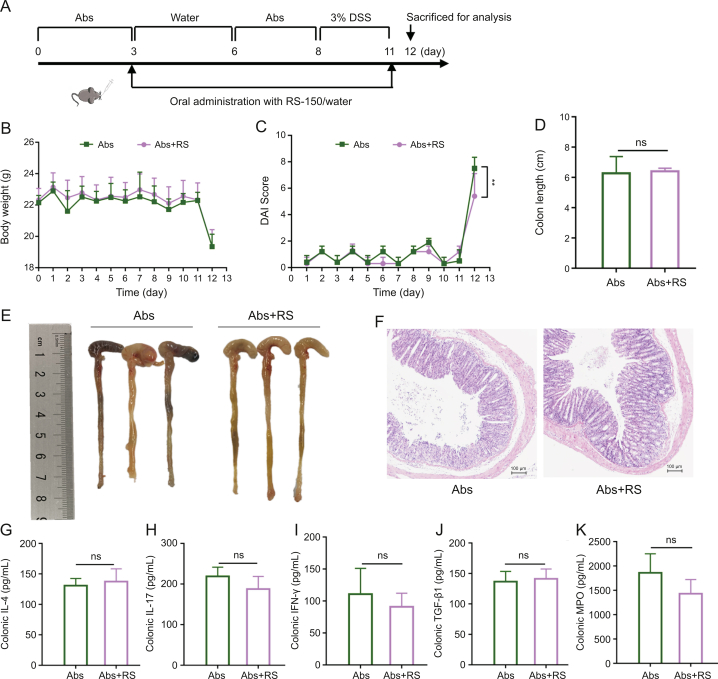
Fig. 9.
Therapeutic effect of R. serra on dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis mice was microbiota dependent. (A) Schematic illustration of the animal experiment design. C57BL/6J mice were pretreated with a broad-spectrum oral antibiotic (Abs) cocktail (100 mg/Kg of vancomycin, 200 mg/Kg of ampicillin, 200 mg/Kg of metronidazole, and 200 mg/Kg of neomycin sulfate) at days 0–3 and 6–8 and then administered with 3% DSS (m/V) for 4 days (days 8–11). The Abs and Abs + R. serra (RS) group were orally administered water and R. serra (150 mg/kg/day) (RS-150) from day 3 to day 11. (B) Body weight changes of each group were monitored daily and expressed as a percentage of initial weight. (C) Disease activity index (DAI) score. (D) Colon length. (E) Morphology of colons. (F) Typical hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained colon tissue sections. Colonic levels of (G) interleukin (IL)-4, (H) IL-17, (I) interferon (IFN)-γ, (J) transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1, and (K) myeloperoxidase (MPO). Abs group: Abs-treated mice administered with water; Abs + RS: Abs-treated mice administered with R. serra extract. P values were analyzed using unpaired t-tests. ∗∗P < 0.01; ns: not significant.