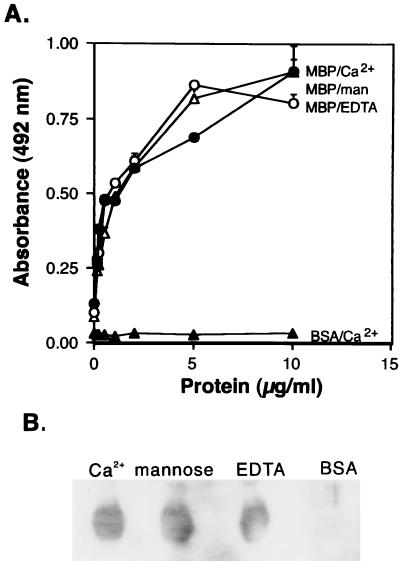
FIG. 2.
Binding of MBP-A to CD14 produced in insect cells. (A) Microtiter well binding. CD14H (10 μg/ml, 50 μl) (●, ▵, ○) produced in insect cells or BSA (▴) was used to coat microtiter wells, which were then incubated with the indicated concentrations of recombinant MBP-A at 37°C overnight in the presence of 5 mM Ca2+ (●). In some experiments, 0.2 M mannose (man) was added to the binding buffer (▵). EDTA (1 mM) was also included instead of Ca2+ (○). The protein binding to CD14H was detected by using polyclonal antibody to MBP-A as described in Materials and Methods. The data shown are means + standard errors of three experiments. (B) Ligand blot analysis. Four micrograms of CD14H produced in insect cells was electrophoresed, and that transferred on the PVDF membranes was incubated with MBP-A (Ca2+) or BSA in the presence of 5 mM Ca2+ at room temperature for 3 h. Mannose (0.2 M) was added to the binding buffer. EDTA (1 mM) was also included instead of 5 mM Ca2+. The MBP-A binding to CD14H was detected with anti-MBP-A IgG as described in Materials and Methods.