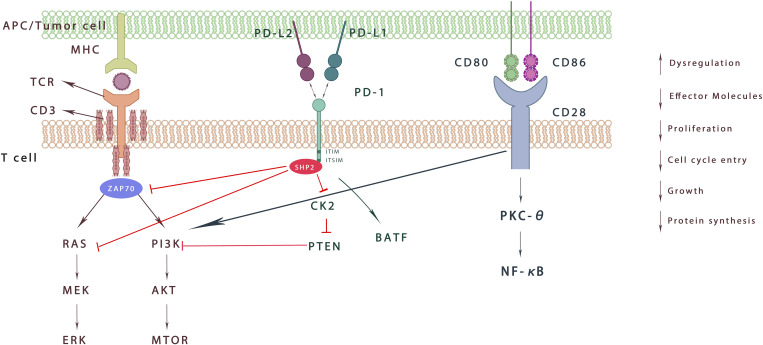
Figure 1.
Effect of PD-1 signaling on T cells. When binding to PD-L1 and PD-L2, ITSM is phosphorylated and recruits SHP-2, which inhibits downstream signaling through dephosphorylated kinases. It further weakens ZAP70 phosphorylation and decreases the RAS-MEK-ERK/PI3K Akt mTOR pathway. In addition, PD-1 activation increases the expression of BATF. Overall, PD-1 signaling aggravates the imbalance of immune microenvironment, inhibits T cell proliferation, decreases effector molecules, and protein synthesis.