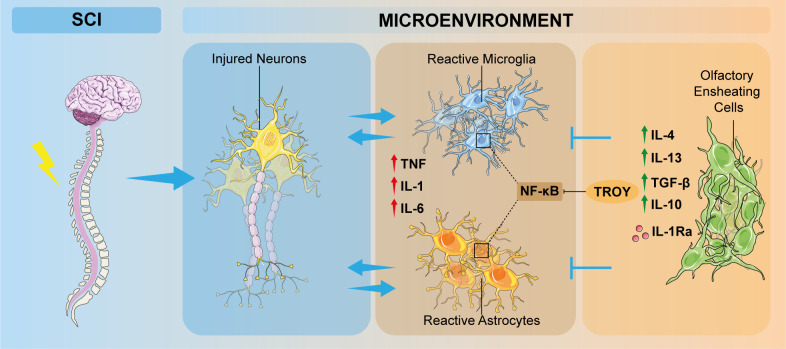
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of the involvement of OECs in inflammation modulation after SCI. Neuronal damage induces pathological increasing of inflammatory responses, which promotes microglia polarization from a resting state to a M1-phenotype and astrocyte activation. OECs are able to modulate these inflammatory events by interacting directly or indirectly with microglia and astrocytes, thus ameliorating the detrimental condition of the altered microenvironment. OEC, olfactory ensheathing cell; SCI, spinal cord injury; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IL, interleukin; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β, IL-1Ra: interleukin-1 receptor antagonist.