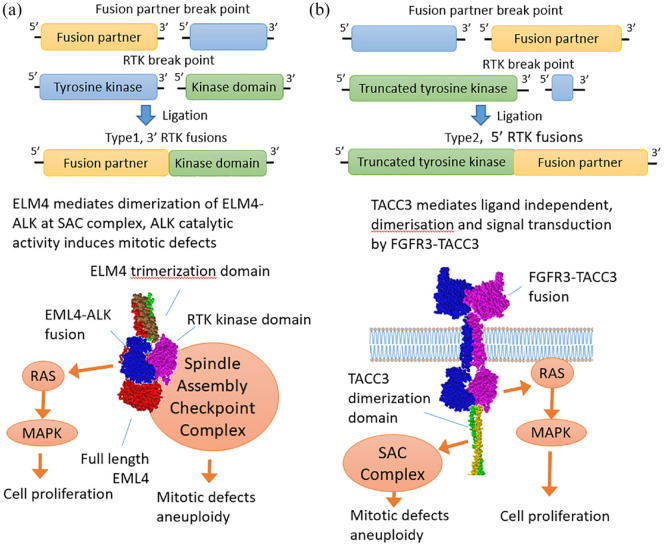
Figure 2.
Structure and functions of the tyrosine kinase gene fusions of the first and second types.109 (a) Type 1 fusion diagram represents a fusion protein between EML4 and ALK retaining the tyrosine kinase domain, whereas the rest of the RTK including transmembrane domain is lost. The resulting chimera translocates into the cytoplasm where it signals in a RAS/MAPK-dependent manner forming lipid-independent protein granules.110,111 ELM4 is a spindle checkpoint protein112 whose trimerization domain is retained in chimeras and most likely mediates interaction with the spindle assembly checkpoint complex and mitotic defects.113,114 (b) Type 2 RTK diagram exemplifies FGFR3-TACC3 chimera in which TACC3 dimerization leucine zipper is attached to the C-terminus of FGFR3 mediating ligand-independent dimerization and signaling. In turn, TACC3 is a spindle checkpoint protein and FGFR3-TACC3 chimera causes mitotic defects.115,116
MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase.