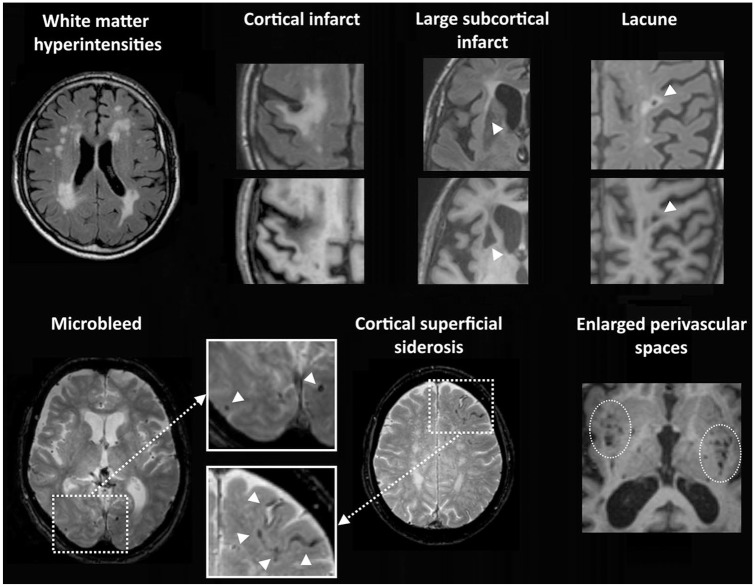
Figure 1.
Vascular lesion types on brain MRI. Top row: white matter hyperintensities are visible as high signal on the Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR) image. Chronic cortical infarcts, large subcortical infarcts, and lacunes of presumed vascular origin are visible as fluid-filled cavities (hypo-intense on the T1 image) with surrounding gliosis (hyperintense signal on the FLAIR image). Bottom row: microbleeds are visible as small sphere-shaped hypo-intense lesions, and cortical superficial siderosis as a hypo-intense rim along the cortical surface on T2*-weighed images. Perivascular spaces in the basal ganglia and subinsular regions are shown as groups of small fluid-filled cavities that follow the orientation of penetrating vessels on this T1-image.