Figure 10.
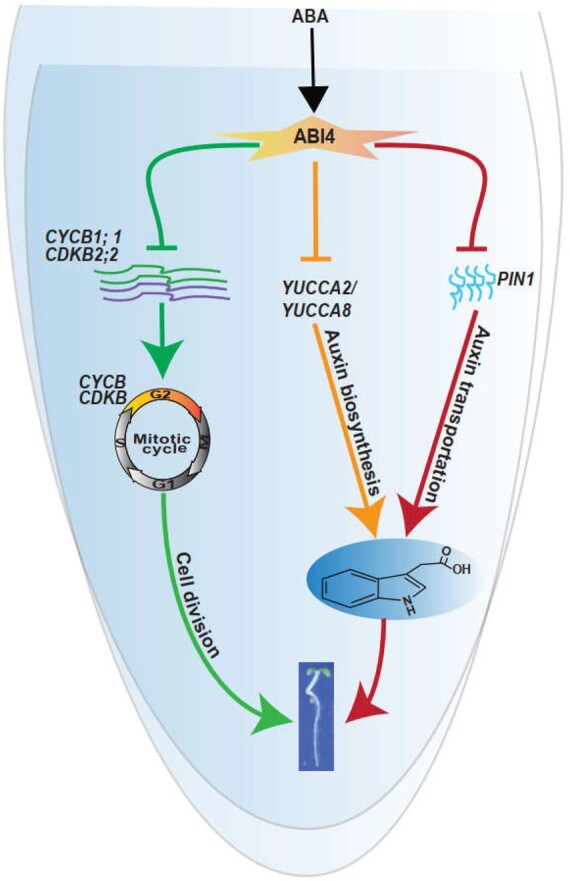
Proposed working model in which ABA represses primary root elongation by impairing the transcription of the ABI4-CYCB1;1/CDKB2;2 regulatory module and auxin biosynthesis. This simplified model showed that exogenous ABA application induces ABI4 transcription in the primary root tip, and the increased level of ABI4 further inhibits the cell cycle cascade by directly reducing CYCB1;1 and CDKB2;2 expression. Concurrently, ABI4 decreases the auxin concentration in the primary root tip by inhibiting the expression of the auxin biosynthesis genes YUCCA2 and YUCCA8, and the auxin transporter encoding gene PIN1. Altogether, the phytohormone ABA inhibits primary root growth through its effects on ABI4-mediated auxin and cell cycle pathways.
