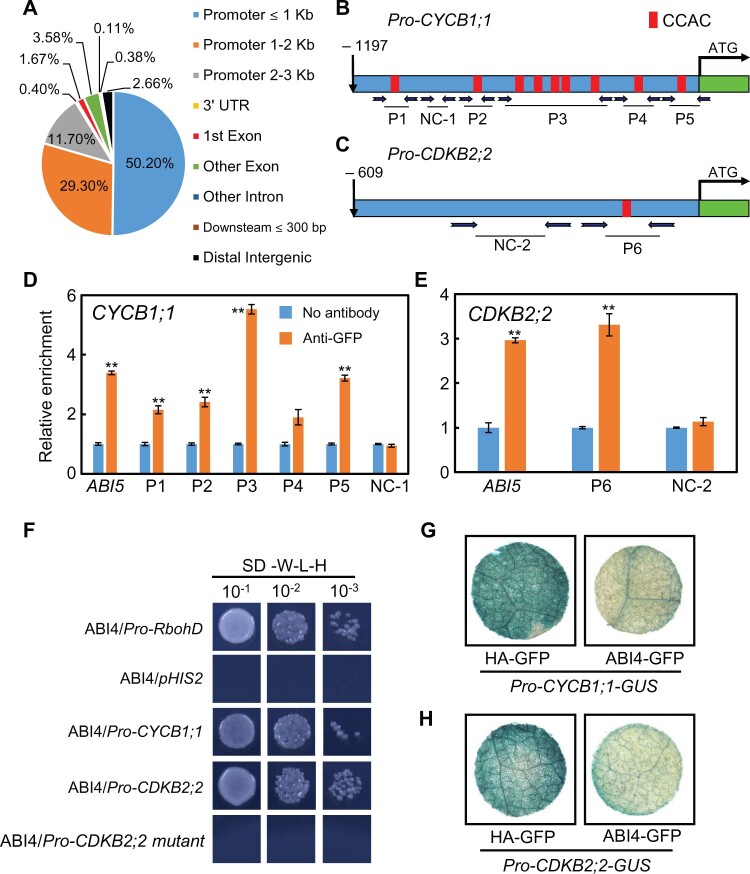
Figure 4.
ABI4 promotes CYCB1;1 and CDKB2;2 transcription by directly binding to their promoters. A, Summary of ChIP-seq results. The pie chart shows where ABI4 binds to the promoter fragments. B and C, Promoter sequence analysis of (B) CYCB1;1 and (C) CDKB2;2. The fragment of 1,197-bp upstream of ATG of CYCB1;1 and 609-bp upstream of the start codon of CDKB2;2, respectively, was determined to be their promoters. D and E, ChIP-qPCR assay was carried out to investigate the association between the ABI4 transcription factor and the (D) CYCB1;1 and (E) CDKB2;2 promoters. Chromatin from the transgenic plant OE-ABI4 was isolated. The promoter fragment of ABI5 was chosen as a positive control, and the promoter region of ACTIN12 was employed as the internal control. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences from no antibody (**P < 0.01). The values are means ± se, n = 4. Statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t test. F, Yeast one-hybrid assay showing the direct interaction between ABI4 and the CYCB1;1 and CDKB2;2 promoters. The full-length promoters were used in this experiment. The promoter region of RbohD was chosen as the positive control. Furthermore, the promoter of CDK2;2 was mutated (information presented in Supplemental Figure S7) and then subjected to yeast one-hybrid analysis. G and H, Nicotiana benthamiana transient expression assay revealed that ABI4 inhibited (G) CYCB1;1 and (H) CDKB2;2 expression in vivo. Representative images of the N. benthamiana leaves are shown.