Figure 4.
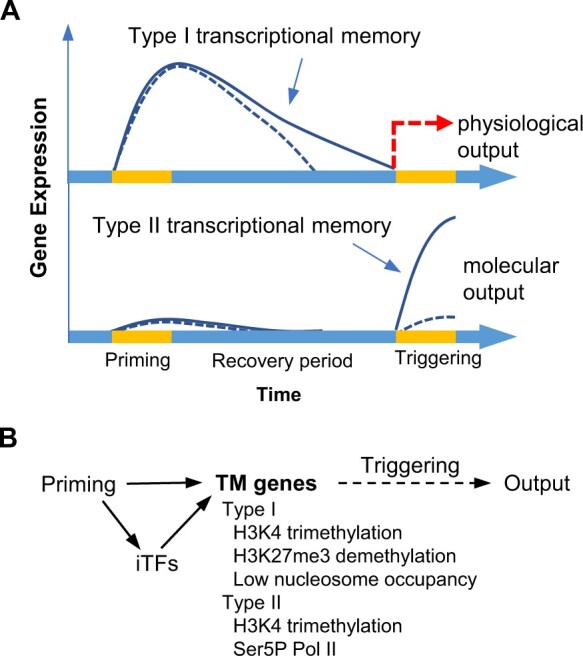
Transcriptional memories formed by abiotic stress priming and transcriptional networks. A, Two types of TM formed by priming. Type I TM enables the persistent expression of TM genes during the recovery period (top panel). Type II TM modifies the expression of TM genes during the triggering session, resulting in stronger and faster expression (bottom panel). The expression behaviors of TM genes in mutants that fail to maintain TM are represented by a dashed line, whereas that of the wild type is represented by a solid line. B, A simplified transcriptional network for the maintenance of TM. Stress-iTFs bind to the promoters of TM genes, resulting in the tri-methylation of histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me3) in both types of TM. The paused form of RNA polymerase II (Ser5P Pol II) accumulates at the promoter regions of Type II TM genes. Both H3K4me3 and Ser5P Pol II are associated with the primed state of TM-II genes. Demethylation of H3K27me3 and low nucleosome occupancy are associated with the sustained expression of Type I TM genes.
