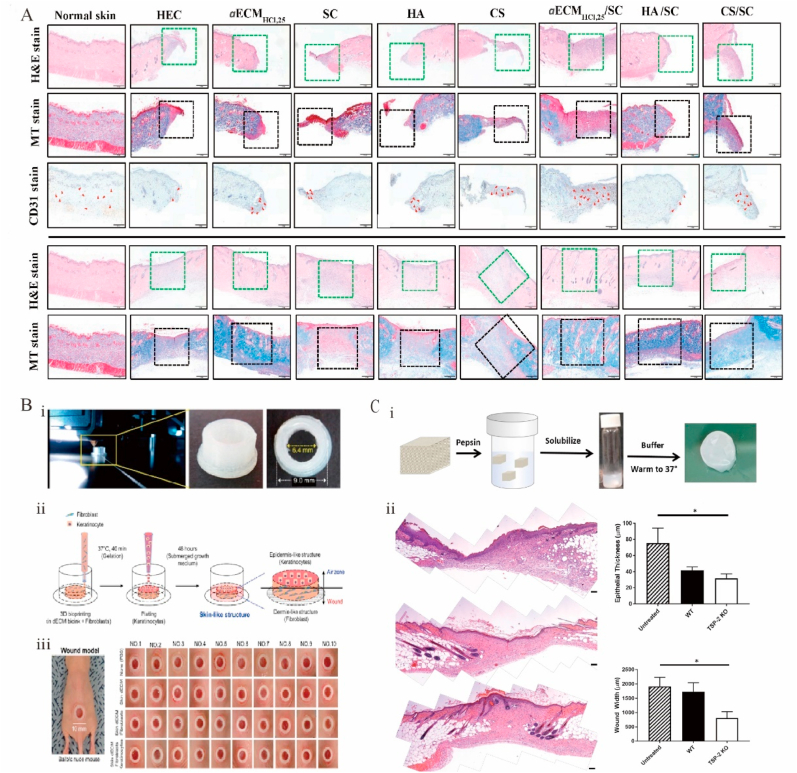
Fig. 5.
Functional decellularized extracellular matrix in the skin repair. (A) Histological analysis of normal skin and wounds treated with different dressings showed that the aECMHCl, 25/SC dressing promotes the healing of diabetic wounds. Adapted reprinted with permission from Ref. [255], based on CC BY License. (B) Skin substitutes and generation of chimney structures through 3D printing. (i, ii) Constructing chimney structures using a 3D printer and creating skin substitutes using 3D cell-printing technology. (iii) Validating uniform chimney model production in all experimental groups. Adapted reprinted with permission from Ref. [262], based on CC BY License. (C) Genetic manipulation allows for tissue-derived hydrogel repair of diabetic skin wounds. (i) A schematic diagram of the hydrogel preparation and example macroscopic images of the hydrogel (ii) Representative suture images of untreated, WT gel treated, or thrombospin-2 knockout gel-treated. Adapted reprinted with permission from Ref. [256]. Copyright © 2018 American Chemical Society.