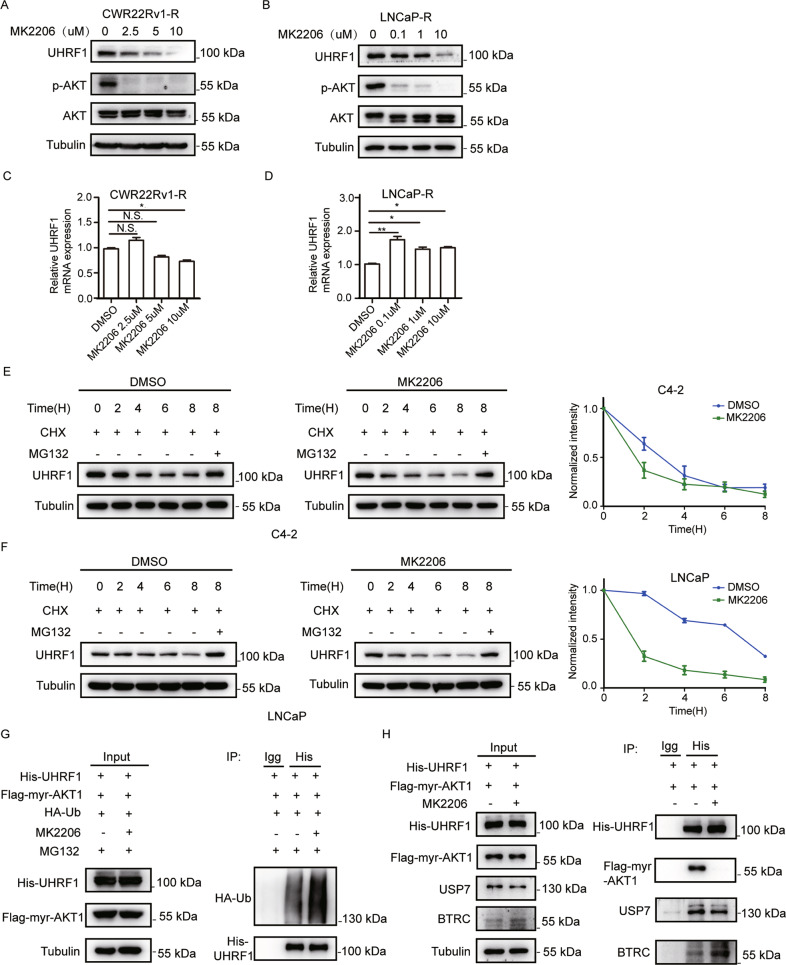
Fig. 3. AKT inhibition promotes the degradation of UHRF1 protein through ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.
A, B CWR22Rv1-R (A) or LNCaP-R cells (B) were treated with stepwise concentrations of MK2206 for 24 h, and the protein levels of UHRF1 or p-AKT were assessed by western blotting. C, D The mRNA levels of UHRF1 were measured by qRT-PCR. E, F C4-2 (E) or LNCaP (F) cells were treated with 10 μM MK2206, together with 50 uM cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated time, or were treated with 10 μM MK2206 plus 50 uM CHX and 50 mM MG132 for 8 h. UHRF1 protein levels were assessed by western blotting and the bands were quantified by image-J software. G HEK-293T cells were co-transfected with the plasmids encoding His-UHRF1, Flag-myr-AKT1, and HA-ubiquitin for 48 h, and then treated with 50 μM MG132 plus 10 μM MK2206 for additional 8 h. UHRF1 protein was immunoprecipitated with ant-His antibody, and the ubiquitinated-UHRF1 were assessed with anti-HA antibody. H HEK-293T cells were co-transfected with the plasmids encoding His-UHRF1 or Flag-myr-AKT1, and then treated with 10 μM MK2206 for 24 h. UHRF1 protein was immunoprecipitated with anti-His antibody, and deubiquitinase USP7 or E3 ubiquitin protein ligase BTRC were measured by western blotting. The presented results were representative of experiments repeated at least three times. Data was represented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.