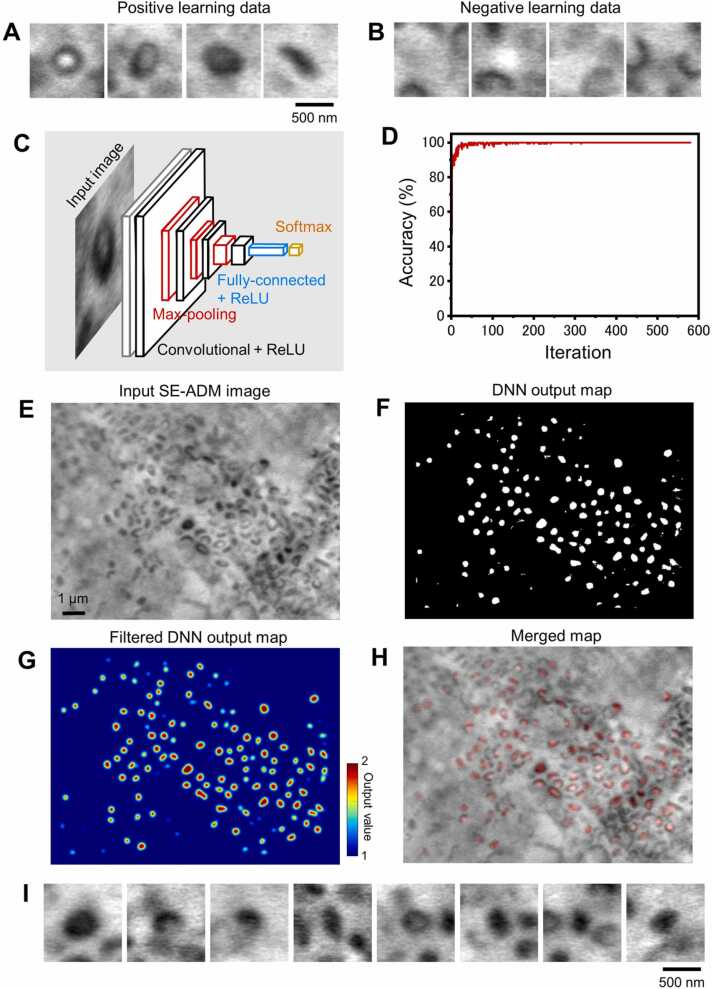
Fig. 5.
Detection and analysis of melanosomes using the DNN system. A) Typical melanosome images of MNT-1 observed by SE-ADM. We manually selected 239 typical images. These images were given as positive learning data to the DNN system. B) Typical non-melanosome images observed by SE-ADM. We manually selected 307 non-melanosome images in the cell. These images were given as negative learning data to the DNN system. C) A schematic diagram of the DNN system. The DNN consists of an input layer, the convolutional layers, Max-pooling layers, and a fully-connected layer with ReLU, and the final output layer is the softmax layer. Details of the DNN are described in Materials and Methods. D) Recognition accuracy for each learning iteration calculated from unlearned 1000 images. After 50 trials, the accuracy reached quite close to 100 %. E) Typical SE-ADM image of MNT-1 cells (10,000 ×) inputs to the DNN system. F) DNN output map for the input image in (E). The output value at the particle position is 2 and 1 otherwise. G) Gaussian filtered DNN output map. The kernel size of the filter is 25 × 25 pixels with σ = 7. H) Merged image of the input image (E) and the Gaussian filtered DNN output (G). Red areas indicate locations of high DNN output. I) Typical SE-ADM melanosome images in MNT-1 cells automatically picked up using the filtered DNN output map of (G). Scale bars, 500 nm in (A, I) and 1 µm in (E).