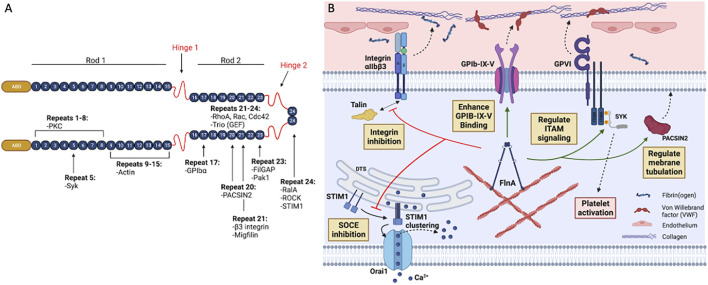
FIGURE 1.
Structure and binding partners of FLNA. (A) FLNA is a 280 kDa homodimer consisting of an actin-binding domain (ABD) at the N-terminus, followed by 24 immunoglobulin (Ig)-like repeat domains folded into β-sheets (numbered 1–24). Two hinge domains, one at Ig repeat 15–16 and another at 23–24, separate the Ig domains into two different rod regions: rod one and rod 2. Rod one consists of Ig repeats 1–15, and rod two consists of Ig repeats 16–23. Dimerization occurs through the interaction of repeat 24. FLNA interacts with many receptors and signaling molecules through its 24 Ig repeats. (B) In platelets, the store-operated calcium entry (SOCE) is regulated by the interaction between STIM1 and Orai1. Upon depletion of Ca2+ storage, STIM1 undergoes a conformational change and multimerizes on the dense tubular system (DTS) membrane. Consequently, STIM1 clusters initiate the assembly of Orai1 subunits in the plasma membrane, forming a Ca2+ channel which leads to the influx of extracellular Ca2+. FLNA downregulates SOCE function by directly interacting with STIM1 in the actin cytoskeleton, thereby abolishing the STIM1-Orai1 interaction. In resting platelets, FLNA has been proposed to constitutively associate with integrin β3 cytoplasmic tail (CT) through its Ig repeat 21. This association blocks the interaction between the β3 CT and talin or kindlin-3, thereby inhibiting integrin αIIbβ3 activation. GPIb-IX-V mediates adhesion of platelets to von Willebrand factor (VWF) upon endothelial injuries. FLNA constitutively interacts with GPIb-IX-V and enhances its binding to VWF. This interaction involves FLNA Ig repeat 17 to the GPIbα CT of GPIb-IX-V. FLNA also positively regulates ITAM- and ITAM-like-containing receptor signaling in platelets by interacting with Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk). This interaction is essential for GPVI receptor signaling, which is an important pathway for collagen-mediated platelet adhesion and activation. FLNA Ig repeat 20 interacts with the F-BAR protein PACSIN2 to regulate membrane tubulation and intracellular membrane architecture in platelets. This interaction also likely contributes to demarcation membrane system (DMS) formation in megakaryocytes. Figure created with BioRender.com.