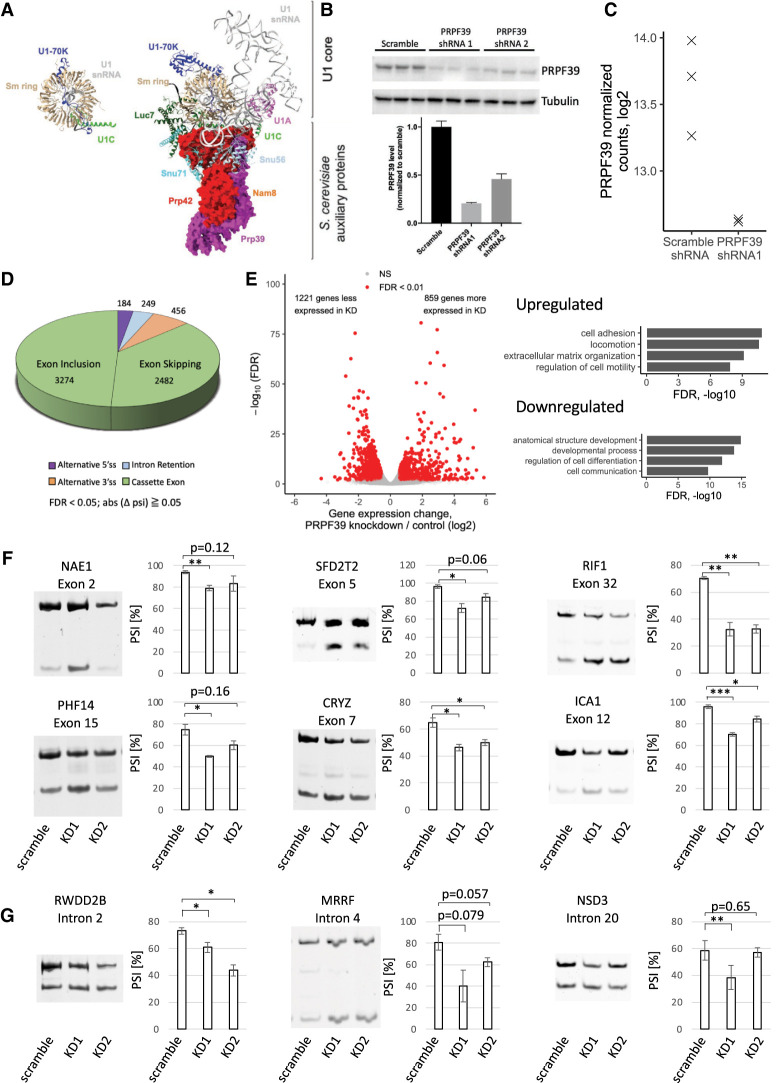
FIGURE 1.
PRPF39 KD affects alternative splicing events. (A) The human U1 snRNP (PDB 4PJO) with coloring to match the yeast U1 snRNP structure (PDB 6N7R). The yeast U1 snRNP shows the interaction between Prp39/Prp42 with U1C and other auxiliary proteins. Prp39/Prp42 are shown in surface representation, and the other proteins and RNAs are shown in ribbon representation. All structural representations in this paper are prepared using Chimera X (Pettersen et al. 2021). (B) Western blot (top) and quantification (bottom) demonstrate PRPF39 KD in HEK293 cells with two shRNAs. (C) Normalized sequencing read counts from RNA-seq analysis show dramatic reduction of PRPF39 mRNA in KD sample. (D) Type and number of alternative splicing events affected by PRPF39 KD. (E) Volcano plot demonstrating the expression changes caused by PRPF39 KD (left) and gene ontology analyses of these changes (right). (F) RT-PCR analyses of selected skipped exon events identified thorough RNA-seq indicate increased short isoform after PRPF39 KD. Standard deviation and statistical significance were derived from three biological replicates of KDs. (*), (**), and (***) denote P < 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001, respectively. (G) RT-PCR analyses of alternative 5′ ss events identified through RNA-seq indicate changed 5′ splice site selection after PRPF39 KD. Standard deviation and statistical significance were derived from three biological replicates of KDs. (*) and (**) denote P < 0.05 and 0.01, respectively.