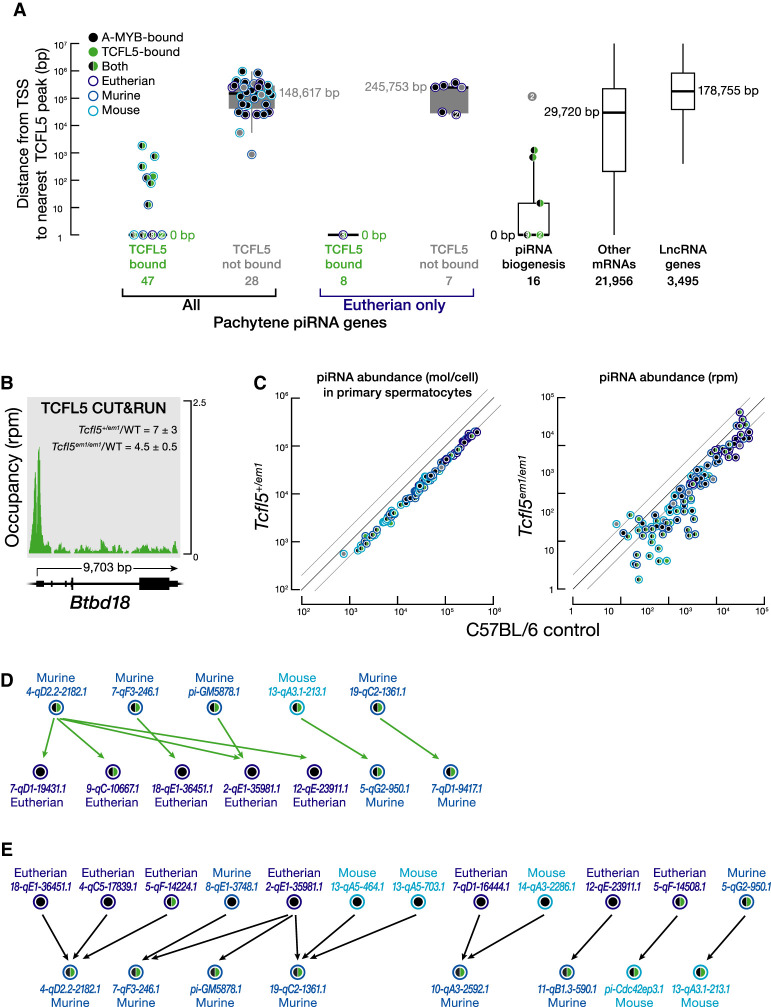
FIGURE 3.
Younger pachytene piRNA genes whose transcription is activated by TCFL5 produce piRNAs that initiate piRNA production in evolutionarily older pachytene piRNA genes. (A) The distance from the nearest TCFL5 peak to the transcription start sites (TSS) of pachytene piRNA genes, genes encoding piRNA biogenesis proteins, and other protein-coding or noncoding genes obtained from CUT&RUN of FACS-purified primary spermatocytes. Horizontal lines: median; whiskers: maximum and minimum values, excluding outliers. Each dot represents distance (mean of two trials) from the nearest TCFL5 peak to the transcription start site of individual genes. Measurements with the same values are indicated by a single marker indicating the number of individual data points. Gpat2, which is required for piRNA biogenesis in flies (Vagin et al. 2013) and in cultured mouse germline stem cells (Shiromoto et al. 2013), was not included in this analysis, because its participation in the piRNA pathway in vivo in mice remains to be established. (B) TCFL5 CUT&RUN peak at the promoter of Btbd18. WT denotes C57BL/6. (C) Steady-state abundance of pachytene piRNAs in primary spermatocytes (left) or whole testes (right) for Tcfl5+/em1 heterozygotes compared to C57BL/6 controls. Each marker represents a pachytene piRNA gene. (D,E) Pachytene piRNA-directed cleavage sites in pachytene piRNA precursor transcripts. In D, each arrow points from the piRNAs derived from a TCFL5-dependent pachytene piRNA gene toward the corresponding cleavage site in a pachytene piRNA precursor transcript whose transcription is activated by A-MYB. TCFL5-dependent genes were defined as those whose promoters were occupied by TCFL5 and whose precursor and piRNA abundance in Tcfl5em1/em1 mutant mice were less than those in C57BL/6. In E, each arrow points from the piRNAs derived from one of 12 A-MYB-dependent pachytene piRNA genes toward genes for which the abundance of pachytene piRNA precursor transcripts was reduced less than twofold in Tcfl5em1/em1 mutant mice. A-MYB-dependent genes were defined as those whose promoters were occupied by A-MYB and whose expression was essentially unchanged in Tcfl5em1/em1 mutant mice.