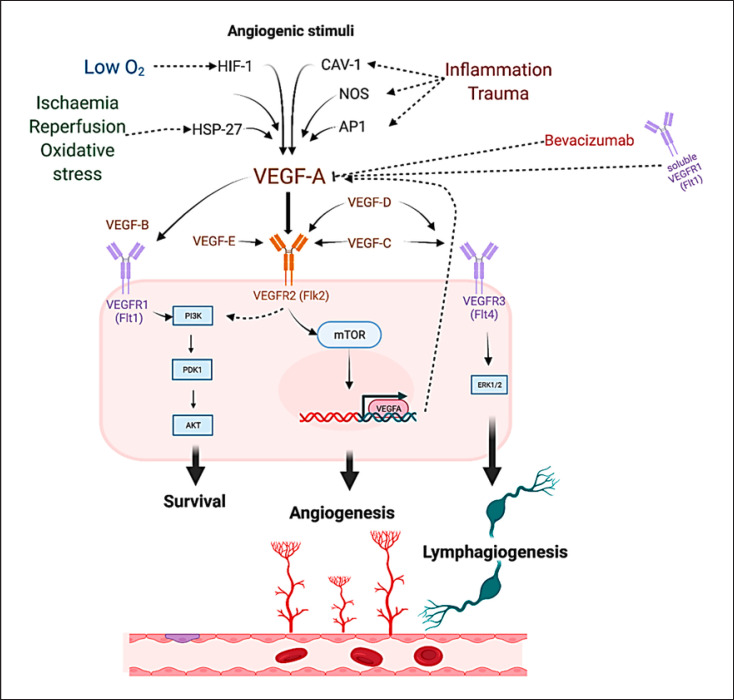
Fig. 3.
Angiogenic stimuli such as hypoxia through hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1); reperfusion ischemia and oxidative stress through heat shock protein 27 (HSP27); tissue trauma, and inflammation though activator protein 1 (AP-1), caveolin-1 (Cav-1), or nitric oxide synthase (NOS) [66, 67] promote VEGF-A activation. Bevacizumab and soluble VEGFR1 exert inhibitory effects upon VEGF-A [14, 71]. Binding of VEGF-A to VEGFR2 activates downstream proangiogenic cascades [14, 51, 52]. VEGF-B is the main substrate of the membrane-bound VEGFR-1, activation of which leads to promotion of cell survival via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Ak strain transforming (PI3K/AKT) pathway with little effect upon angiogenesis [68, 69]. VEGF-C and VEGF-D are primary substrates of the VEGFR3 receptor, activation of which leads to lymphangiogenic promotion via the extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) pathway [70, 71, 72]. Cross-activation of the VEGF receptors is possible by multiple VEGF family members with variable effects still to be fully elucidated [14].