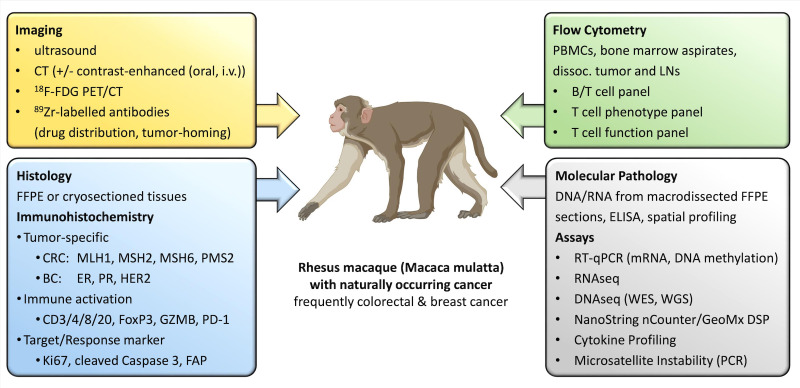
Figure 2.
Diagnostics, biomarkers, and assays currently employed in TBMs. A multitude of methods can be used to diagnose cancer in TBM, classify the suspicious lesion, and follow-up treatment response. This includes versatile imaging methods, tumor-specific Immunohistochemistry panels, molecular pathological tests, as well as the follow-up of the immunological response in the tumor bed, lymph nodes, and peripheral blood by flow cytometry (created with BioRender). BC, breast cancer; CRC, colorectal cancer; DNAseq, DNA sequencing; ER, estrogen receptor; FAP, fibroblast activation protein; FDG, fluorodeoxyglucose; FFPE, formalin fixed paraffin embedded; i.v., intravenous; LNs, lymph nodes; mRNA, messenger RNA; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PD-1, programmed cell death protein-1; PET, positron emission tomography; PR, progesterone receptor; RNAseq, RNA sequencing; RT-qPCR, real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; TBM, tumor-bearing monkey; WES, whole exome sequencing; WGS, whole genome sequencing.