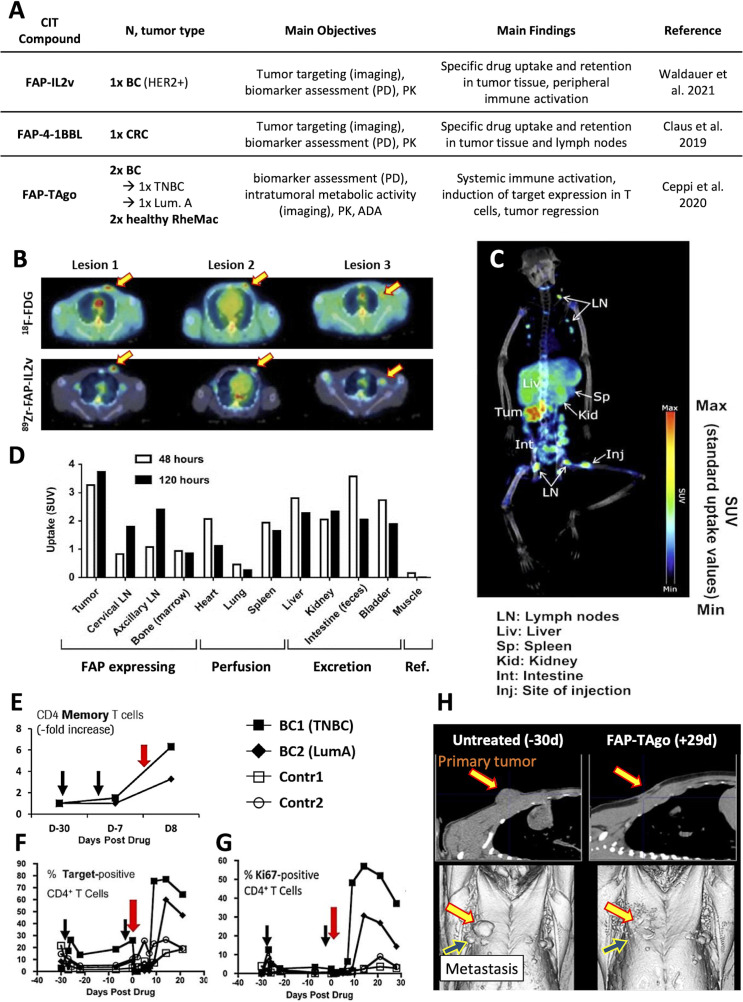
Figure 3.
Preclinical studies on CIT agents performed in TBM. (A) Several novel bispecifics were tested in TBM and confirmed tumor-homing of the CIT agent as shown in (B) for FAP-IL2v (lesions highlighted by arrows) in a BC-bearing rhesus-macaques. (C) tumor-homing was also demonstrated for FAP-4–1-BBL (lesion highlighted by an arrow) in a CRC-bearing rhesus macaque and (D) the tissue distribution over time determined. (E) Diphtheria/pertussis/tetanus vaccination in combination with FAP-TAgo induced an expansion of tumorous CD4+ memory T cells in BC-bearing rhesus macaques and a strong expansion of peripheral target-positive (F) CD4+ T cells and (G) Ki67+CD4+ T cells. (H) a strong radiographic response was observed in BC2 with no nodules regrowing >12 months later. BC1 had lung metastases at the time of treatment which responded initially (not shown) but reached her humane endpoint soon after. (Illustrations adapted from83–85). ADA, anti-drug antibody; BC, breast cancer; CIT, cancer immunotherapy; CRC, colorectal cancer; FAP, fibroblast activation protein; FDG, fluorodeoxyglucose; LNs, lymph nodes; PD, pharmacodynamics; PK, pharmacokinetics; RheMac, rhesus macaques; SUV, standardized uptake value; TBM, tumor-bearing monkey; TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer.