Figure 6. Knockdown of IGFBP2 decreases Akt phosphorylation and suppresses the proliferation and spheroid formation of normal fallopian tube epithelium.
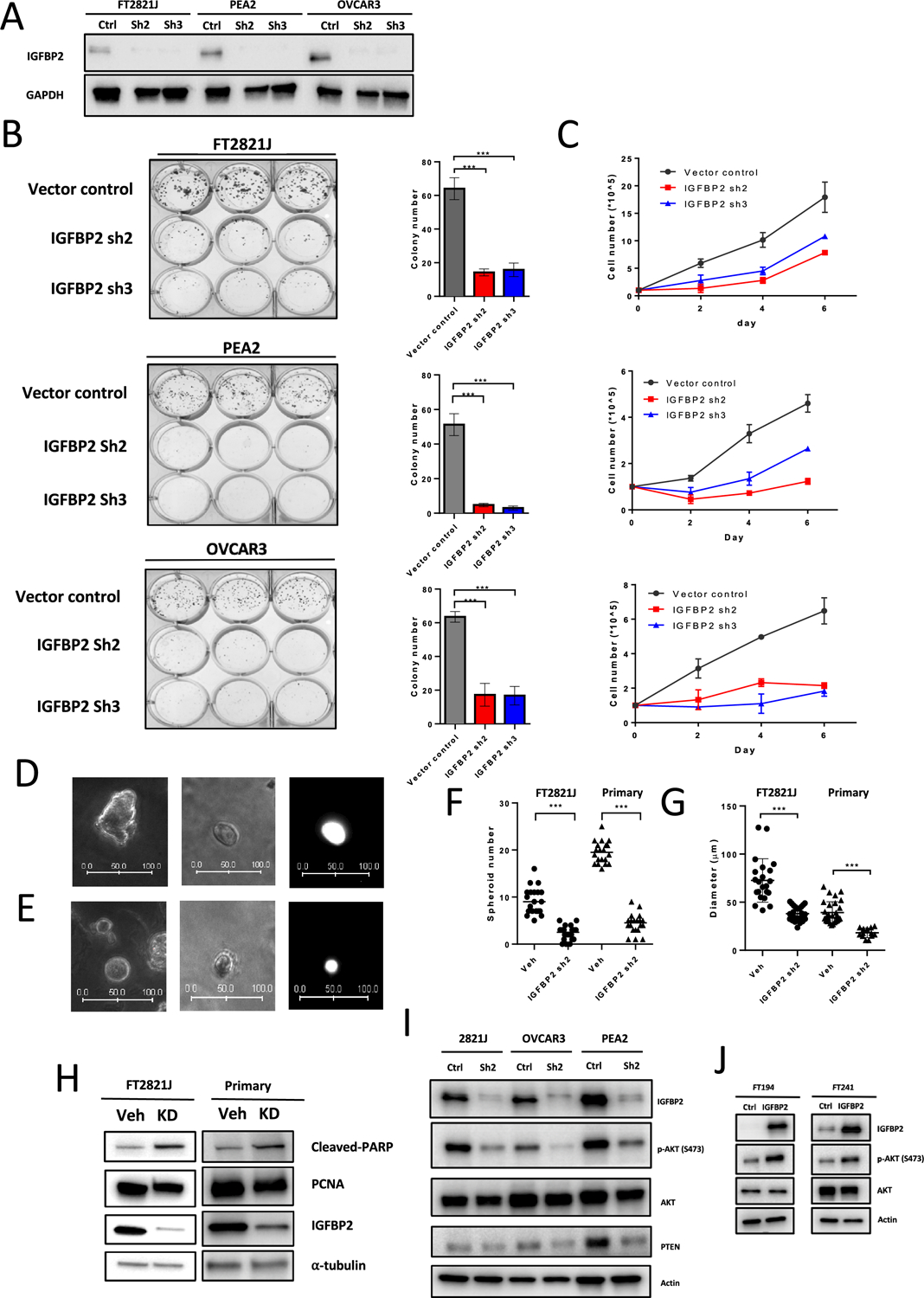
(A) Immunoblots of IGFBP2 from FT2821J, PEA2, and OVCAR3 cell lines after IGFBP2 shRNA lentivirus knockdown. (B) (left) Colony formation assays in FT2821J, PEA2, and OVCAR3 cells after IGFBP2 knockdown. (right) Quantification of data from left panel. (C) Cell proliferation assays after IGFBP2 knockdown in FT2821J, PEA2, and OVCAR3 cells. (D-E) Representative images of FT2821J spheroids. (left) Vehicle control. (middle) IGFBP2 knockdown. (right) GFP fluorescence image of the spheroid shown in the middle panel. Scale bar units, μm. (F-G) Scatter plots showing the number (F) and diameter (G) of spheroids after knockdown of IGFBP2 in FT2821J and primary FTE cells. (H) Immunoblots showing expression of cleaved-PARP, PCNA, IGFBP2, and α-tubulin (loading control) in extracts from FT2821J cells and primary cultures of fallopian tube epithelium after treatment with IGFBP2 shRNA lentivirus for 3 days. (I) Knockdown of IGFBP2 in IGFBP2-high cell lines reduces Akt phosphorylation but less PTEN expression. (J) Overexpression of IGFBP2 induces Akt phosphorylation in IGFBP2-low FTE cell lines (FT194 and FT241).
