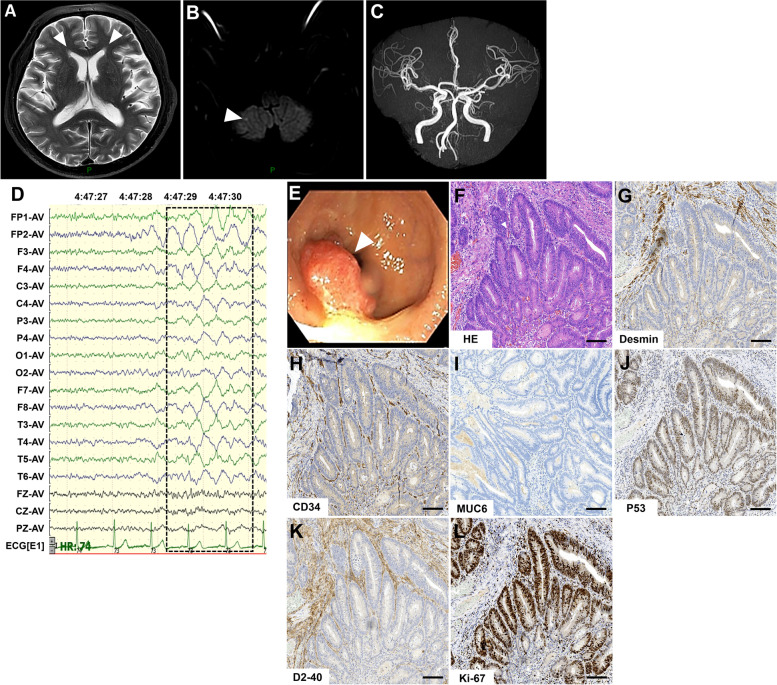
Fig. 1.
Magnetic resonance imaging, electroencephalogram and pathological findings. A, B and C Brain magnetic resonance imaging shows symmetric hyperdense on T2-weighted images around the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle and slightly restricted speckle diffusion signals in the right cerebellum on the diffusion-weighted image; angiography sequences showed spinal basilar artery tortuousness and mild cerebral arteriosclerosis. D Electroencephalogram shows that during the wakeful phase, moderate slow waves of about 2–2.5 HZ can be seen in each lead (frame), and no epilepsy waves are seen during the waking period and during sleep. E Colonoscopy shows that the rectum is about 6 cm from the anus to the entrance, and the surface is hyperemic and eroded. F Hematoxylin & eosin staining shows glandular fusion. Necrotic substances are seen in the glandular cavity and have infiltrated into the submucosal layer. Elongated or vacuole-like nuclei can be observed, as well as nuclear fission. G-L Immunohistochemistry shows positive for staining of Desmin, P53, Ki-67 (area for 40–50%), CD34 and D2–40. MUC6 staining is negative. Bar = 100μm