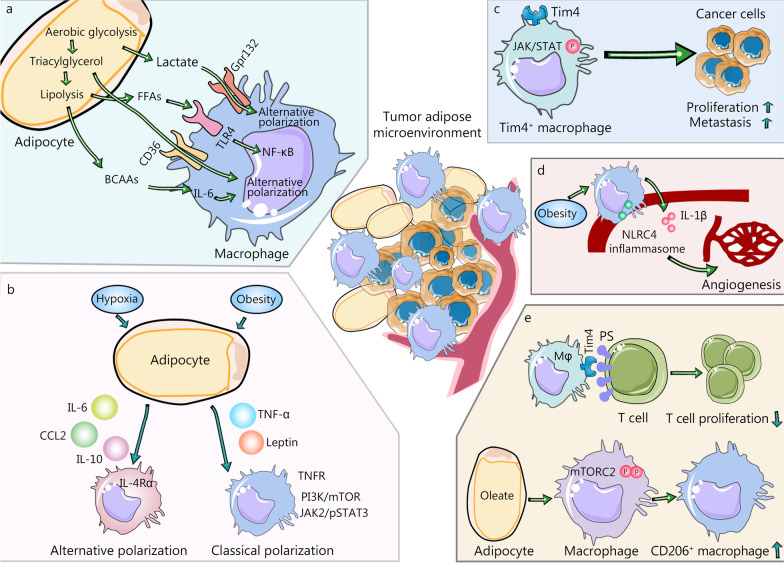
Fig. 1.
Polarization of ATMs is induced by metabolites and inflammatory factors derived from tumor adipose microenvironment (TAME). a Function and polarization of macrophages in TAME are regulated by metabolites, derived from glycolysis, lipid metabolism, and amino acid metabolism. Lactate from aerobic glycolysis promotes the alternative polarization of macrophages. Free fatty acids (FFAs) activate the toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 and increase the expression of proinflammatory genes dependent on nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB). Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), another metabolite from triacylglycerol lipolysis, participate in inducing immune-suppressing macrophages. b Polarization of ATMs is also regulated by inflammatory factors. For example, leptin activated the JAK2/pSTAT3 pathway to function as a proinflammatory factor. Leptin-activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway in macrophages to increase the production of lipid droplets and induce the classical polarization of macrophages. In contrast, M2 stimuli such as IL-6, IL-10, and CCL2, trigger alternative macrophage polarization. CCL2 promotes the production of IL-10 and increases the generation of M2-associated markers. c Tumor macroenvironment has a fundamental effect on tumor growth and metastasis. Tim4+ ATMs have a high level of activation of JAK/STAT signaling and promoted the progression and metastasis of ovarian cancer. d Obesity results in the activation of NLRC4 inflammasome in macrophages to increase their infiltration and the generation of IL-1β. In turn, IL-1β contributes to elevated angiogenesis. e Though integrating with CD8+ T cells with PS overexpression, Tim4+ macrophages suppress their proliferation and make them away from tumor targets. Oleate, one of the long-chain unsaturated fatty acids, amplifies the immunosuppressive effects of TAMs by inducing the polarization of macrophages into the CD206+ suppressive subtype by hyper-phosphorylating mTORC2. ATMs adipose tissue macrophages, BCAAs branched-chain amino acids, CCL2 chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2, IL-1β interleukin-1beta, IL-10 interleukin-10, IL-6 interleukin-6, mTORC2 mTOR complex 2, NF-κB nuclear factor kappa B, NLRC4 NOD-like receptor (NLR) family CARD-containing protein 4, PS phosphatidylserine, TAM tumor-associated macrophage, TLR toll-like receptor, TNF-α Tumor necrosis factor-α, TNFR TNF-α receptor