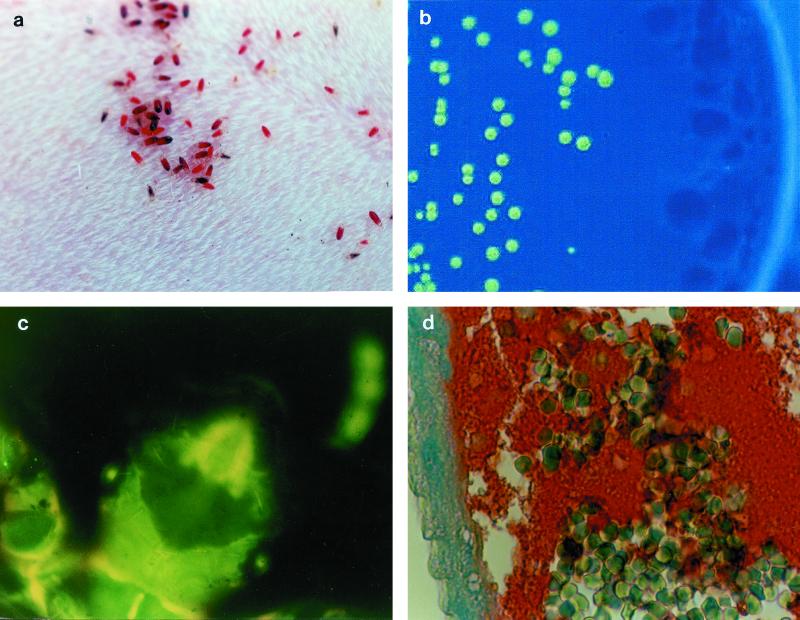
FIG. 1.
Experimental model of body louse infection by GFP-expressing B. quintana. (a) Pediculus humanus humanus feeding on a rabbit; (b) fluorescent colony isolated on selective agar from an infected louse 10 days after the initial infection; (c) autofluorescence of body lice; (d) immunohistological detection of B. quintana. Note the numerous erythrocytes and the clusters of bartonellae in the intestine lumen (red clumps) and against the intestine wall (blue). Streptavidin-biotin-peroxidase method, polyclonal rabbit anti-B. quintana used at a dilution of 1:400, hemalun counterstain. Magnification, ×660.