Figure 3.
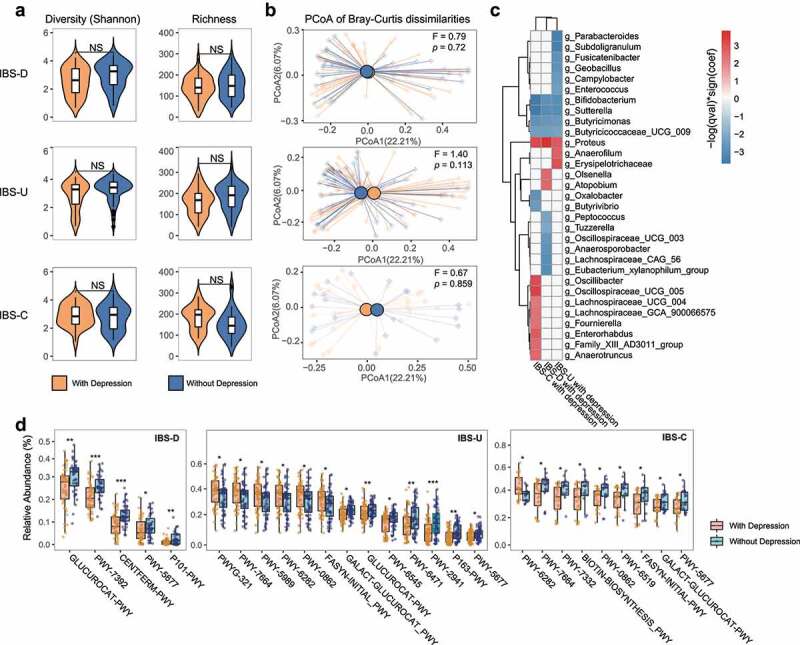
Bacterial and functional alterations in gut microbiota of IBS patients with depression. (a) Diversity (Shannon Index) and richness of gut microbiota of IBS patients with depression or without depression in different subtypes, NS means not significant. (b) Principal Coordinates Analysis of gut microbiota composition of IBS patients with depression corresponding IBS patients without depression in different subtypes by Bray-Curtis dissimilarities, the difference among IBS subtypes was assessed by PERMANOVA test. (c) The association between gut microbiota and IBS patients with depression in different subtypes. The association was assessed by the multivariate analysis by linear models (MaAsLin; p < .05, FDR<0.1). (d) MetaCyc pathway differences between IBS patients with depression and those without depression, * p < .05, ** p < .01, *** p < .001, **** p < .0001. In each subtype, an equal number of IBS patients without depression were selected using the established matching algorithm.
